What is the dark web?
The dark web is the part of the internet where users can access unindexed web content anonymously through special web browsers like The Onion Router (Tor). Though the dark web is popularly associated with illegal activities, it is also used by the intelligence community, whistleblowers, members of the media, and ordinary citizens whose communication may be monitored or restricted by the government.
Open web vs deep web vs dark web
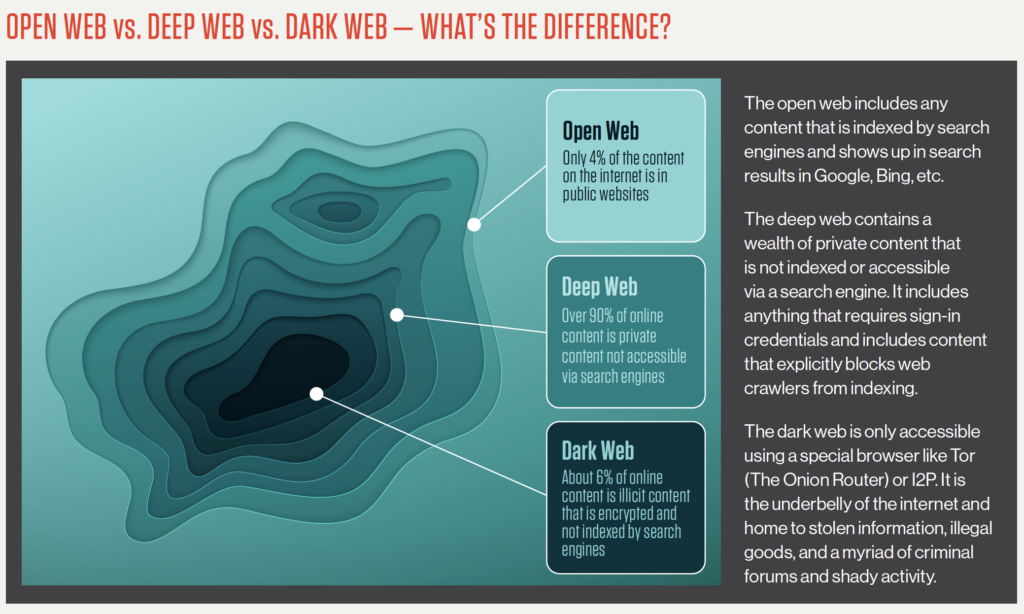
Source: Exposing the Open, Deep, and Dark Web
Though the terms dark web and deep web are often used interchangeably, they are two distinct concepts. The open web is the public counterpoint to the deep and dark web.
Open or surface web definition
The open web, also called the surface web, includes any public web content that is indexed by search engines. Webpages on the open web will show up in search results on sites like Google and Bing. Though a large volume of traffic visits on the open web every day, it only represents 4% of the content on the internet.
Deep web definition
The deep web refers to any web content that is not indexed or pages that can’t be found with a search engine. Examples of the deep web include any websites that are behind a paywall or require login credentials. Most internet users access the deep web several times a day to perform common tasks, such as checking email, accessing a bank account, or reviewing health or school records. The deep web constitutes over 90% of online content and is inaccessible via search engines.
Dark web definition
The dark web is a network of unindexed web content. The biggest differentiator between the deep and dark web is that dark web activity is made anonymous through a variety of encryption and routing techniques.
The dark web is also unregulated, meaning that it is run and upheld by a vast network of individuals around the world. This network contains thousands of volunteers who operate proxy servers to route dark web requests. As such, no one is responsible for setting rules or ensuring their adherence. This operating model is what makes the dark web such a valuable and appealing tool for cybercriminals and other people with questionable intentions.
Though the dark web is part of the deep web, the inverse is not true. As such, the two terms should not be conflated.

How to Expose the Open, Deep, and Dark Webs
Download this white paper to learn how CrowdStrike Falcon® Intelligence Recon can help identify potentially malicious and criminal activity across the dark web.
Download NowThe history of the dark web
The origins of the dark web can be traced to researchers and scientists in the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory who, in 2002, recognized how easily digital activity and communication could be monitored, intercepted, and exploited. It grew out of a need for a more secure communications channel in the intelligence community, despite the fact that it is often associated with nefarious activities today.
The dark web continues to be a valuable tool and exchange network for many groups around the world. Some consider it an outright necessity, as it helps encourage free speech, maintain a free press, and support the work of law enforcement and government agencies.
What can you find on the dark web?
The dark web contains a wide variety of services and content, some of which skirts or disregards legality. Though the intention and purpose of users on the dark web may vary, the dark web itself is neither good nor bad.
Law enforcement agencies, the intelligence community, and cybersecurity professionals often maintain a presence on the dark web in an attempt to monitor, trace, or trap cybercriminals. Simply knowing what information is being bought and sold online may help organizations and people take the appropriate steps to protect their information and assets.
Dark web price index
According to the 2023 dark web price index, these are typical prices, in U.S. dollars, of goods and services sold on the dark web:
- Credit card details, account balance up to $5K: $125
- Stolen online banking logins, minimum of $2K in account: $60
- Western Union transfer from stolen account above $1K: $32
- U.S.-verified LocalBitcoins account: $70
- SoundCloud plays x1K: $1
- Hacked Facebook account: $25
- Hacked Gmail account: $60
- Netflix account (one-year subscription): $20
- Fake U.S. Green Card: $450
- 10 million U.S. email addresses: $120
- U.K. passport template: $22
- Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack on unprotected website, 10-50K requests per second, one week: $350

2024 CrowdStrike Global Threat Report
The 2024 Global Threat Report unveils an alarming rise in covert activity and a cyber threat landscape dominated by stealth. Data theft, cloud breaches, and malware-free attacks are on the rise. Read about how adversaries continue to adapt despite advancements in detection technology.
Download NowDark web commerce and cryptocurrency
Transactions on the dark web are conducted with cryptocurrency due to its decentralized and anonymous nature. Cryptocurrency enables buyers and sellers to exchange goods and services without revealing their identities, making it ideal for illegal activities.
Bitcoin is the most widely recognized and utilized cryptocurrency on the dark web. However, as law enforcement agencies have developed better methods to trace Bitcoin transactions, other cryptocurrencies with enhanced privacy features have gained popularity, such as Monero (XMR), Zcash (ZEC), and Litecoin (LTC).
Despite its legitimate uses, cryptocurrency’s untraceable payment nature has raised concerns around money laundering and illicit trade, driving regulatory scrutiny.
Is the dark web dangerous?
The dark web is a common gathering place for hackers and other cybercriminals, which can make browsing the dark web a risky activity. Visitors to the dark web should exercise extreme caution when downloading files, as they may infect your devices with viruses, malware, trojans, ransomware, or other malicious files. At a minimum, users should ensure that their cybersecurity defenses are activated and up to date.
That said, many of the actors on the dark web are highly skilled digital adversaries who can easily outmaneuver basic security measures. As a leading cybersecurity vendor, CrowdStrike cautions all organizations and individuals to refrain from using the dark web.
Is the dark web illegal?
Similar to using a standard web browser to access the open web, the act of using Tor or a dark web browser to access the dark web is not illegal in and of itself. It is illegal to perform illegal acts on the dark web, regardless of the level of anonymity provided by the platform. As of a 2020 estimate, about 57% of the dark web is illegal.
Users of the dark web should also realize that although their activity is technically anonymous, associating with people who are conducting illegal activities can have legal implications. Recent high-profile takedowns of dark web marketplaces such as Silk Road, AlphaBay, and Wall Street Market have resulted in hundreds of arrests around the world, underscoring the risks of engaging in illegal activity in any form.

2024 Threat Hunting Report
In the CrowdStrike 2024 Threat Hunting Report, CrowdStrike unveils the latest tactics of 245+ modern adversaries and shows how these adversaries continue to evolve and emulate legitimate user behavior. Get insights to help stop breaches here.
Download NowAdvantages and disadvantages of the dark web
The dark web offers both benefits and risks for users going into it, but the intent of the user will also impact this. Here’s a breakdown of the key pros and cons.
| 1. Anonymity and Privacy | Users can communicate and browse privately, protecting against censorship and surveillance. | 1. Illegal Activities | The dark web is a hub for the illicit trade of things like drugs, weapons, and stolen data. |
| 2. Platform for Whistleblowers | Journalists and activists can use the dark web to share sensitive information securely. | 2. Scams and Malware. | Users are at risk of falling victim to scams and malware attacks. |
| 3. Access to Specialized Content | The dark web includes niche communities, research, and ad-free search engines. | 3. Potential Legal Risks | Law enforcement actively monitors illegal activities. |
How to access the dark web
To access the dark web, users need a special browser. The most common of these browsers is Tor, which launched in 2002 and serves millions of users. Another is the Invisible Internet Project (I2P), which specializes in the anonymous hosting of websites on the dark web.
Once a user installs a dark web browser on a device, it functions like a regular browser. That said, it can be difficult for users to find the material they are looking for on the dark web. Addresses tend to be a mix of random numbers and letters, making them challenging to remember or access manually. Addresses also change frequently due to the transient nature of many dark web actors. Finally, because the dark web routes all traffic through a series of proxy servers, which are operated by thousands of volunteers around the world, the search process is typically very slow.
How to protect yourself on the dark web
To protect yourself from the risks associated with the dark web, it's essential to take proactive security measures.
Here are some practical steps you can implement to safeguard your personal information:
- Use identity theft protection services to monitor your personal data
- Regularly change your passwords and store them securely using a password manager
- Enable two-factor authentication on all important accounts
- Avoid sharing unnecessary personal information online
- Stay alert to phishing attempts
- Monitor your credit reports and consider freezing your credit to prevent unauthorized access
If you discover your data on the dark web, act quickly to minimize the damage and report the incident to relevant authorities to ensure any necessary legal action is taken.
How CrowdStrike can help you
Knowing if your information is on the dark web is a critical part of protecting yourself from threats. Dark web monitoring tools are similar to a search engine (like Google) for the dark web. These tools help find leaked or stolen information such as compromised passwords, breached credentials, intellectual property, and other sensitive data that is being shared and sold among malicious actors operating on the dark web.
Learn how CrowdStrike can help protect your brand and data with CrowdStrike Falcon® Adversary Intelligence.







