What is phishing?
Phishing is a cyberattack that impersonates a reputable person or organization with the intent to deploy ransomware, steal existing account credentials, acquire enough information to open a new fraudulent account, or simply to compromise an endpoint. A single click on a malicious phishing link has the potential to create any of these problems.
What is a phishing email?
The most common form of phishing attack is a phishing email. With hundreds of billions of emails sent and received each day, it’s getting more difficult to tell which ones are real and which ones might be phishing attempts.
Anatomy of a phishing email
 Example phishing email attack
Example phishing email attack
How to spot a phishing email?
Phishing emails will typically contain at least one of the following telltale signs:
- Asks for Sensitive Information
- Uses a Different Domain
- Contains Links that Don't Match the Domain
- Includes Unsolicited Attachments
- Is Not Personalized
- Uses Poor Spelling and Grammar
- Tries to Panic the Recipient
Learn More
As cybercrime of all kinds, and phishing, in particular, reaches new heights in 2023, it’s important for every person in your organization to be able to identify a phishing attack and play an active role in keeping the business and your customers safe.
1. Asks for sensitive information
Legitimate businesses will never request credit card information, social security numbers or passwords by email. If they do, it’s likely to be a scam – like the below:
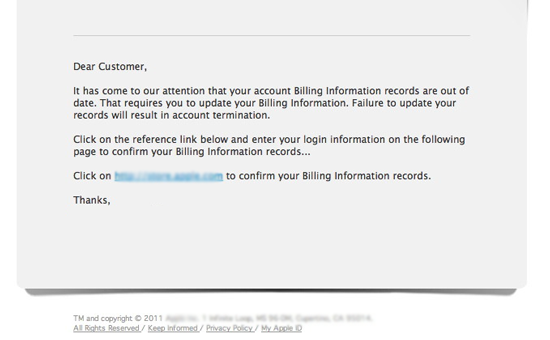 Source - https://cba.ca/Assets/CBA/Images/Article-detail-images/updateBillingEmail-en.png
Source - https://cba.ca/Assets/CBA/Images/Article-detail-images/updateBillingEmail-en.png2. Uses a different domain
Phishing scams often attempt to impersonate legitimate companies. Make sure the email is sent from a verified domain by checking the ‘sent’ field. For example, a message from Amazon will come from @amazon.com. It won’t come from @clients.amazon.org, like this phishing example:
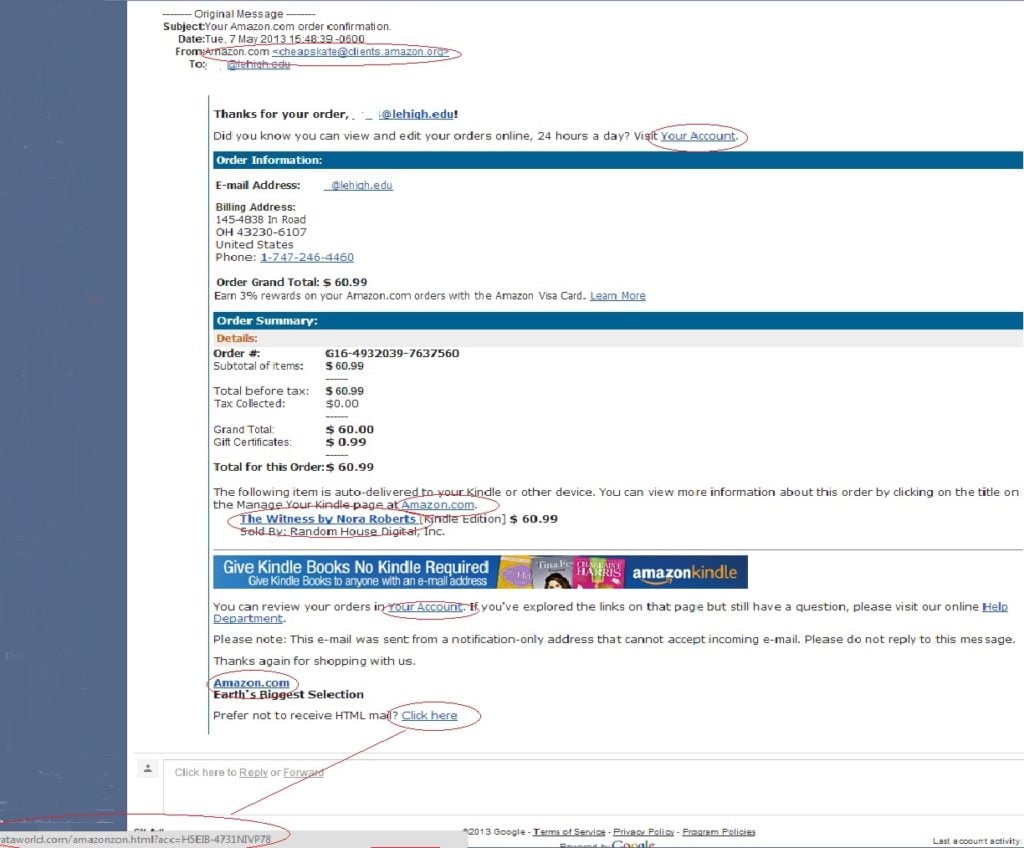 Source - https://lts.lehigh.edu/sites/lts.lehigh.edu/files/phishing20130508.jpg
Source - https://lts.lehigh.edu/sites/lts.lehigh.edu/files/phishing20130508.jpg3. Contains links that don’t match the domain
In the above Amazon phishing example, you’ll also see the links don’t actually take you to the Amazon domain.
Hover the cursor over any links to make sure they will take you to the site you expect. Also, look for https:// at the start of the URL, and do not click links that do not use HTTPS.
4. Includes unsolicited attachments
A legitimate company will never attach or expect you to download files from their emails. It will instead direct you to its site, where you can download documents safely.
Avoid opening email attachments, even from a supposed well-known organization.
5. Is not personalized
Companies that do legitimate business – or whom you’ve shopped with previously – will know your name. And they will use it, rather than addressing you in a generic manner, such as “Dear Valued Member”, “Dear Customer” or just “Hello”.
6. Uses poor spelling and grammar
Official organizations employ specialist copywriters for their communications. They would never send out emails with obvious spelling or grammar errors, like this Apple phishing email example:
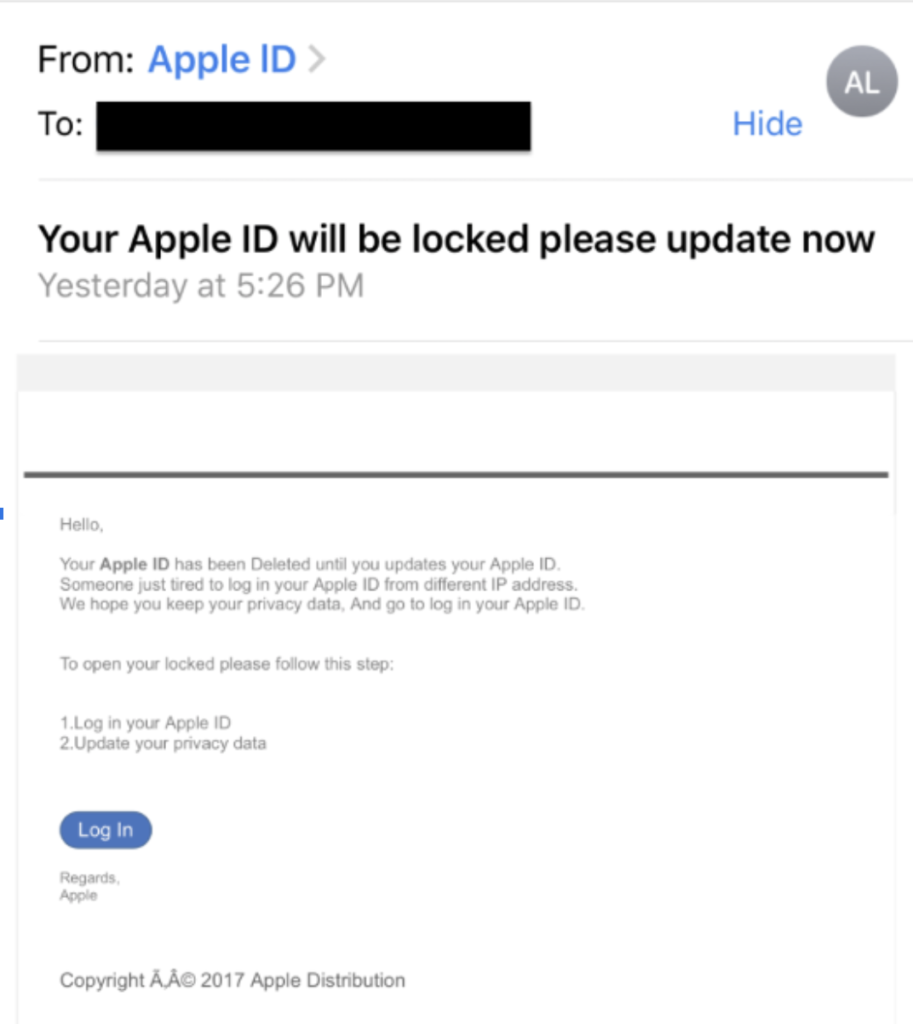
However, hackers aren’t simply bad spellers. The suspicion is that attackers deliberately use grammatical errors to weed out less cautious users, who make easier targets.
7. Tries to panic the recipient
Most phishing attacks try to panic the receiver with urgent, seemingly time-sensitive calls to action. The aim is to make recipients feel as if they’re missing out on an urgent offer or reward, or nervous about the threat of punishment.
Below are some of the common phrases and tactics used by scammers to get you to urgently click on malicious links or attachments:
- We’ve noticed some suspicious activity or log-in attempts
- There’s a problem with your account or payment information
- You must confirm some personal information
- You need to make a payment
- You’re eligible to register or receive a refund
- Offering coupons for free products
- Issuing a fake order confirmation
The fictional example below highlights a common scammer request to update personal information due to abnormal account activity:

If you spot any of these common signs of phishing emails, don’t interact with any links or attachments.
Forward the email to the government’s Anti-Phishing Working Group at reportphishing@apwg.org and delete the email immediately after.





