What is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is a security framework that mandates stringent identity verification for every user and device attempting to access resources, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the organization’s network. Unlike traditional security models that rely on a defined network perimeter, Zero Trust operates on the principle that no user or system should be automatically trusted. Instead, continuous authentication, authorization, and validation of security configurations are required before access is granted to applications and data.
Key concepts of Zero Trust
- No assumed trust: Zero Trust operates under the assumption that threats could exist both inside and outside the network. Therefore, it continuously verifies the identity and security posture of every user and device before granting access.
- Comprehensive security: The framework is designed to secure modern digital infrastructures that may include a mix of local networks, cloud-based environments, and hybrid models. This flexibility makes it suitable for organizations with remote workers, organizations with diverse cloud environments, or organizations facing sophisticated threats like ransomware.
- Continuous monitoring: Zero Trust requires constant monitoring and validation — not just at the point of entry but throughout the duration of a session. This helps organizations detect and respond to potential threats in real time.

The Complete Guide to Building an Identity Protection Strategy
Take the first step toward a resilient identity security posture and download the Complete Guide to Building an Identity Protection Strategy to protect your organization’s digital identity landscape today.
Download NowZero Trust and industry standards
Zero Trust is a broad concept, and its implementation can vary. However, aligning with established standards like the example below can help organizations adopt a more consistent and effective approach.
NIST 800-207: The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) developed this standard as a comprehensive guide for implementing Zero Trust. It is widely recognized for being vendor-neutral and applicable across various sectors, not just government.
By adhering to the NIST 800-207 standard, organizations can ensure their Zero Trust architecture is robust against modern cyber threats and adaptable to cloud-first, remote work environments.
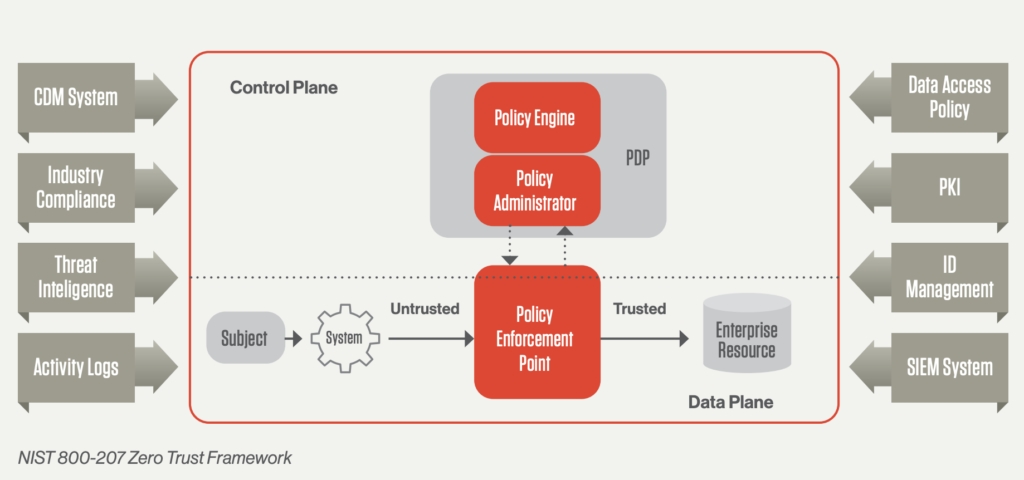
Source: Streamline Your Zero trust Journey Report
Core principles of the Zero Trust model based on NIST 800-207
The Zero Trust model, as outlined in the NIST 800-207 framework, revolves around three core principles designed to enhance security by fundamentally rethinking how trust and access are managed within an organization:
1. Continuously Verify
“Never trust, always verify” is the foundational tenet of Zero Trust. This principle requires that no entity — whether it is a user, device, or application — is trusted by default, regardless of whether it is inside or outside the network perimeter. Verification must be applied continuously and dynamically to ensure that access is granted based on real-time risk assessments.
- Risk-based conditional access: Access should be granted based on a dynamic evaluation of risk, ensuring that only users and devices that meet security requirements can proceed. This approach minimizes disruptions to the user experience while maintaining high security standards.
- Rapid and scalable policy deployment: Policies must be able to adapt quickly to changes in workloads, data, and user locations. This includes accounting for compliance and IT requirements to ensure that security measures do not compromise organizational obligations.
2. Limit the Blast Radius
In the event of a breach, minimizing the damage or “blast radius” is crucial. Zero Trust limits the reach of any potential attacker by restricting their movement within the network, giving security teams time to respond and contain the incident.
- Identity-based segmentation: Traditional network segmentation can be cumbersome and hard to maintain, especially as the environment evolves. Identity-based segmentation provides a more flexible and effective way to control access, as it is tied directly to the identity of the user or device rather than static network boundaries.
- Principle of least privilege: This principle dictates that accounts (including service accounts) should have the minimum permissions necessary to perform their tasks. As tasks or roles change, so should the scope of access. This reduces the risk of over-privileged accounts being exploited by attackers.
3. Automate Context Collection and Response
Effective security decisions require comprehensive data from across the IT environment. Zero Trust emphasizes the automation of context collection and real-time response to ensure that the security system can react swiftly and accurately to potential threats.
Comprehensive Data Collection: Information should be gathered from various sources, including:
- User credentials: Both human and non-human (e.g., service accounts, privileged accounts).
- Workloads: Virtual machines (VMs), containers, and hybrid deployments.
- Endpoints: All devices accessing data.
- Network traffic: Monitoring network activity for anomalies.
- Data access: Tracking who is accessing what data and how.
- Integration with other security systems: This includes APIs that connect to security information and event management (SIEM) systems, single sign-on (SSO) services, identity providers (like Active Directory), and threat intelligence platforms. This integration ensures that the collected data is actionable, enabling the organization to respond to threats in real time.
By adhering to these principles, organizations can create a robust Zero Trust environment that not only protects against known threats but adapts to emerging risks, ensuring a secure and resilient IT infrastructure.

CrowdStrike Falcon and NIST Compliance
Download this report produced by leading compliance assessor Coalfire, and learn how technical security features and capabilities of the CrowdStrike Falcon platform can assist organizations in their compliance efforts with respect to NIST.
Download NowHow Zero Trust works
The implementation of a Zero Trust framework requires the integration of advanced technologies, including:
- Risk-based multi-factor authentication (MFA): Verifies the identities of users and systems based on their risk profile at any given moment.
- Identity protection: Ensures that the identities of users and systems are secured and consistently verified.
- Next-generation endpoint security: Protects endpoints with cutting-edge security measures, preventing unauthorized access and attacks.
- Cloud workload technology: Maintains security across cloud environments, ensuring that workloads are protected from breaches.
In addition to these technologies, Zero Trust necessitates the encryption of data, secure email communication, and the verification of asset and endpoint hygiene before users connect to applications.
Stages of implementing Zero Trust
Zero Trust implementation can be approached in stages tailored to your organization's specific needs:
Visualize: Identify all resources and their access points, and map out potential risks.
Mitigate: Detect and stop threats, or at least minimize their impact when they occur.
Optimize: Expand protection across the entire IT infrastructure while optimizing the user experience.
The shift from traditional network security
Zero Trust represents a significant shift from traditional network security models that relied on a “trust but verify” approach. In the traditional model, users and endpoints within an organization's perimeter were automatically trusted, exposing the organization to risks from both malicious insiders and compromised credentials. This model became increasingly obsolete with the widespread adoption of cloud-based services and the acceleration of remote work due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Continuous monitoring and validation
Under the Zero Trust architecture, organizations must continuously monitor and validate that users and their devices have the appropriate privileges and attributes. This approach goes beyond one-time validation, recognizing that threats and user attributes are dynamic and can change rapidly. Key elements of continuous monitoring include:
- User identity and credential type: Differentiating between human and programmatic credentials.
- Credential privileges: Assessing the level of privileges associated with each device.
- Behavior patterns: Analyzing normal connection patterns for each credential and device.
- Endpoint characteristics: Considering hardware type, function, and firmware versions.
- Geolocation: Tracking the physical location of devices.
- Security protocols: Evaluating authentication protocols, risk factors, operating system versions, and installed applications.
- Incident detection: Detecting and responding to suspicious activities and potential attacks.
Leveraging analytics for enhanced security
To effectively enforce Zero Trust policies, organizations must leverage advanced analytics, drawing on vast datasets of enterprise telemetry and threat intelligence. This data-driven approach enhances AI/machine learning (ML) model training, enabling more accurate policy responses and better protection against breaches.
Organizations should also assess their IT infrastructure and potential attack paths, implementing measures such as segmentation by device types, identity, or group functions to contain attacks and minimize their impact. For instance, protocols like Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) or Remote Procedure Call (RPC) should be tightly controlled, with access limited to specific credentials.
Protecting against credential-based attacks
Zero Trust architecture places a strong emphasis on protecting credentials and data. This includes securing email communications, utilizing secure web gateways (cloud access security broker providers), and enforcing strict password security protocols. By doing so, organizations can ensure the integrity of accounts, adhere to organizational rules, and avoid the risks associated with shadow IT services.
Immediate benefits of Zero Trust for your organization
Zero Trust is beneficial for any organization, but organizations can gain immediate advantages if they must protect an infrastructure deployment model that includes:
- Multi-cloud, hybrid, and multi-identity environments
- Unmanaged devices
- Legacy systems
- Software as a service (SaaS) applications
Additionally, Zero Trust is essential if your organization needs to address the following key threat use cases:
Ransomware: This involves two primary threats, code execution and identity compromise. Zero Trust ensures that if code or an identity is breached, the other is still protected.
Supply chain attacks: These often involve unmanaged devices and privileged users working remotely, both of which are vulnerabilities that Zero Trust can mitigate.
Insider threats: With the challenge of analyzing behavioral data for remote users, Zero Trust's continuous verification process helps identify and mitigate insider threats.
Organizational considerations for Zero Trust
Your organization should also consider the following factors when implementing Zero Trust:
- SOC/analyst expertise: Zero Trust can compensate for challenges in SOC expertise by automating many security processes.
- User experience: Implementing Zero Trust — particularly with MFA — requires careful consideration of the user experience to avoid disruptions.
- Compliance requirements: Whether due to industry regulations or mandates like the U.S. government’s Zero Trust requirements, compliance is a critical driver for Zero Trust adoption.
- Cyber insurance: The rapidly changing cyber insurance market makes Zero Trust an essential strategy for retaining coverage.
Expert Tip
When you invest in a Zero Trust solution, can that solution reduce security complexity, save money, and reduce time to identify and remediate breaches? The answer is a resounding 'YES'! Watch this webcast to explore real-life use cases for Zero Trust that affect your profit margin and overhead to support the whole program.
Why choose CrowdStrike for Zero Trust?
CrowdStrike provides a comprehensive Zero Trust solution that is:
- Frictionless: Designed to integrate seamlessly into existing workflows, reducing complexity and user friction.
- Hyper-accurate: Leveraging advanced AI/ML to provide precise threat detection and automated responses.
- Cost-efficient: Reducing the need for extensive hardware, software, and personnel investments by utilizing cloud-native technologies.
CrowdStrike’s Zero Trust approach ensures that your organization can achieve superior security outcomes while managing costs and maintaining a high standard of operational efficiency. This is particularly crucial as the security landscape continues to evolve with new and more complex threats.
Zero Trust FAQs
Q: What is Zero Trust?
A: Zero Trust is a security framework that mandates stringent identity verification for every user and device attempting to access resources, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the organization’s network.
Q: Who invented the term "Zero Trust"?
A: The term “Zero Trust” was coined by Forrester Research analyst and thought-leader John Kindervag, and follows the motto, "never trust, always verify." His ground-breaking point of view was based on the assumption that risk is an inherent factor both inside and outside the network.
Q: What are the key concepts of Zero Trust?
A: The key concepts of Zero Trust are to always operate under the assumption that a threat exists, enact a comprehensive security framework designed to secure modern and complex security infrastructures, and continuously monitor for threats throughout user sessions.
Q: What are the Zero Trust principles of NIST?
A: Zero Trust revolves around several key principles outlined in the NIST guidelines like continuous verification, limiting the blast radius, and automating context collection and response.
Q: What are the benefits of zero trust?
A: Zero Trust is essential if your organization needs to address cyber threats like ransomware, supply chain attacks, and insider threats, especially if they must protect an infrastructure deployment that includes complex environments, unmanaged devices, legacy systems, and SaaS application.
Q: Why choose CrowdStrike for Zero Trust?
A: CrowdStrike’s Zero Trust approach ensures that your organization can achieve superior security outcomes while managing costs and maintaining a high standard of operational efficiency. This is particularly crucial as the security landscape continues to evolve with new and more complex threats.








