Last week, CISA added CVE-2024-1086 to its Known Exploited Vulnerability Catalog. CVE-2024-1086, a use-after-free vulnerability in the Linux kernel’s netfilter, was disclosed on January 31, 2024 and assigned a CVSS of 7.8 (High). If successfully exploited, it could allow threat actors to achieve local privilege escalation.
While there was no evidence of active exploitation at the time of disclosure, we have since observed adversaries targeting CVE-2024-1086 in the wild. Let’s take a closer look at the events that have unfolded in the past few months:
- March 26, 2024: The security researcher who disclosed CVE-2024-1086 released a blog post describing how to exploit the vulnerability and posted a proof-of-concept (POC) exploit on GitHub.
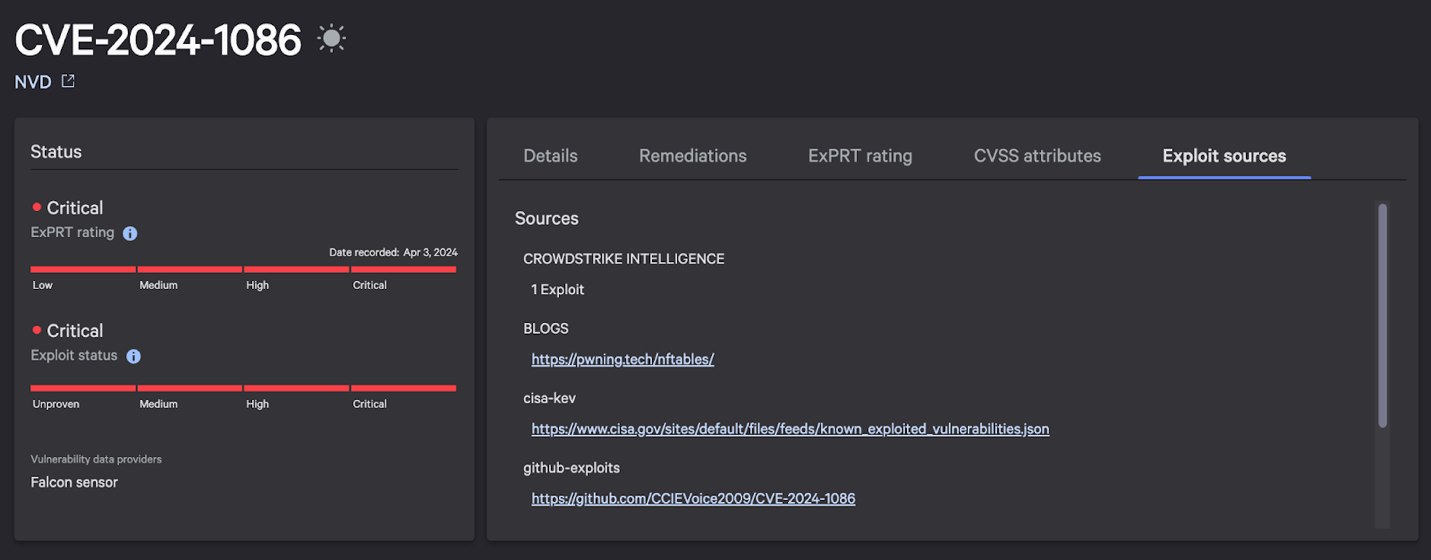
- April 3, 2024: CrowdStrike’s ExPRT.AI, our proprietary vulnerability rating system, automatically upgraded the severity of CVE-2024-1086 to Critical, indicating a very high likelihood of future exploit activity.
- Mid-April 2024: The CrowdStrike Falcon® Adversary OverWatch threat hunting team and CrowdStrike Falcon® Complete managed detection and response team observed two unknown threat actors attempting to leverage CVE-2024-1086. CrowdStrike’s behavior detection (IOAs) and machine learning prevented the exploit attempt and provided extensive coverage for initial access attempts and post-exploitation techniques.
- May 30, 2024: CISA added CVE-2024-1086 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog.
In this blog, we share the details of this vulnerability and how our customers are protected from exploitation.
Overview of CVE-2024-1086
Based on the impacted kernel versions, this vulnerability potentially affects major enterprise Linux distributions (Debian, Ubuntu, Red Hat, Fedora, Amazon Linux, Oracle Linux, Rocky Linux and others) depending on the distribution’s specific configurations and patch levels. As of this writing, most major Linux distributions have released new versions fixing this vulnerability.
CVE-2024-1086 is caused by an nf_tables component flaw in the Linux kernel packet-filtering framework netfilter. Netfilter allows the chaining of multiple rules when processing a packet. After each rule, the verdict value indicates whether processing continues or the packet should be dropped. Due to a reverted commit in the netfilter code, Nf_hook_slow (in core.c) assumes that the upper 16 bits of NF_DROP verdicts contain a valid errno, i.e. -EPERM, -EHOSTUNREACH or similar, or 0.
However, the nft_verdict_init() function interprets the verdict as NF_DROP, eventually causing deallocation of the packet in the nf_hook_slow() function. Later, the verdict resembles NF_ACCEPT, leading to further processing of the packet and ultimately causing a double-free vulnerability.
On March 26, 2024, the security researcher who disclosed CVE-2024-1086 released a blog post describing how to exploit the vulnerability and posted a proof-of-concept (POC) exploit on GitHub. CrowdStrike Counter Adversary Operations confirmed the POC successfully achieved local privilege escalation (LPE) in a test environment.
As noted by the exploit developer, leveraging this POC is dependent on the kernel’s unprivileged user namespaces feature accessing nf_tables. This access is enabled by default on Debian, Ubuntu and kernel capture-the-flag (CTF) distributions. An attacker can then trigger the double-free vulnerability, scan the physical memory for the kernel base address, bypass kernel address-space layout randomization (KASLR) and access the modprobe_path kernel variable with read/write privileges. After overwriting the modprobe_path, the exploit drops a root shell.
While this exploit is stable in a testing environment, real-world target exploitation may impact stability (depending on the targeted environment). CrowdStrike Counter Adversary Operations also revealed the targeted Linux host becomes unstable after closure of the root shell, which is dropped by the exploit. This instability eventually causes the system to crash. However, a more sophisticated threat actor — a targeted intrusion actor, for example — can almost certainly modify the exploit to prevent the system from crashing post-exploitation.
Assess Your Vulnerability with Falcon Exposure Management
CVE-2024-1086, patched in late January 2024, affects the following Linux kernel versions:
- From 6.7 and before 6.7.3
- From 6.2 and before 6.6.15
- From 3.15 and before 6.1.76
- 6.8-rc1
Customers can find CVE-2024-1086 with CrowdStrike Falcon® Exposure Management or CrowdStrike Falcon® Spotlight vulnerability management, as indicated in the below image.
Falcon Exposure Management has had detections for all supported platforms since the vulnerability was initially disclosed. The vulnerability currently has an ExPRT.AI severity rating of “Critical,” with an Exploit Status of “Actively Used (Critical).”
To identify vulnerable systems, navigate to the Exposure Management > Vulnerability Management > Vulnerabilities page in the CrowdStrike Falcon® platform. From there, use the Vulnerability ID filter with a value of “CVE-2024-1086.” If any of the managed systems are vulnerable, results will be shown here. If you receive the message “No vulnerabilities found,” then all of your managed Linux systems have the necessary patches. For any systems found vulnerable, the remediation guidance provided for that system will mention the necessary packages to update.
CrowdStrike Protects Customers from CVE-2024-1086
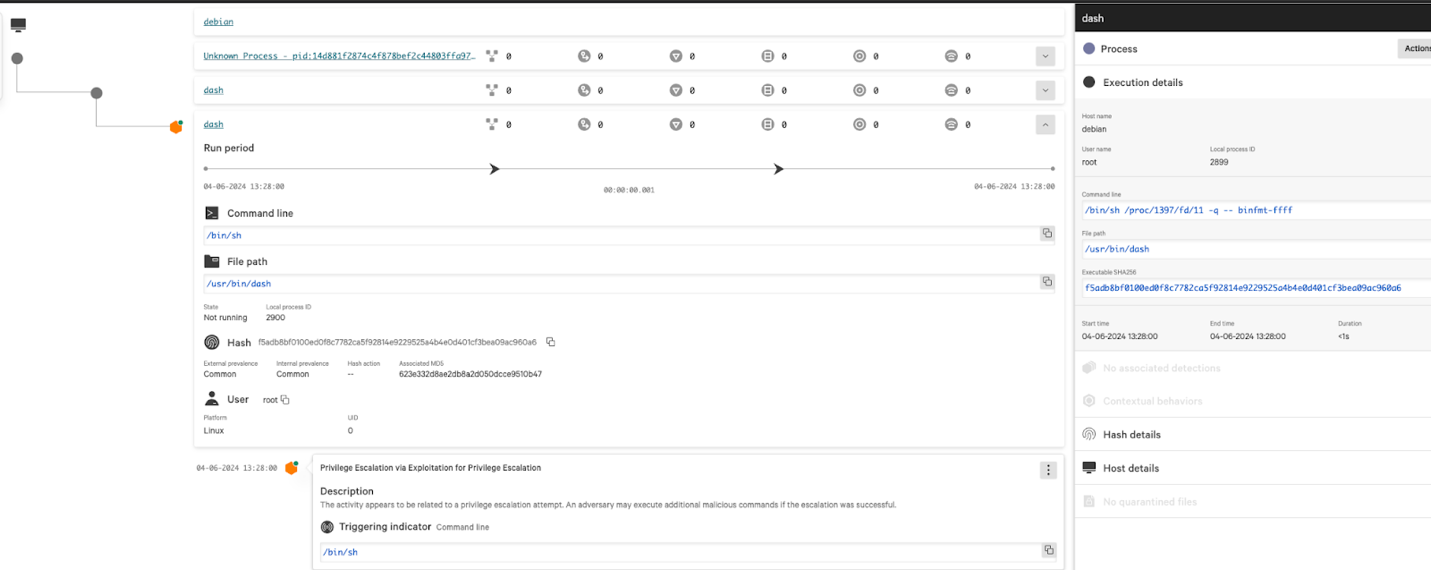
CrowdStrike employs a layered approach for malware detection using machine learning and indicators of attack. To exploit this privilege escalation vulnerability, an adversary requires initial access and will follow up with post-exploitation techniques. Our existing IOAs have extensive coverage for initial access and post-exploitation techniques and will help to prevent those attempts.
In addition, CrowdStrike has released IOAs to prevent the execution of suspicious commands used to elevate privileges by leveraging the use-after-free vulnerability.
Please note that these require the “suspicious processes” Linux prevention policy to be enabled.
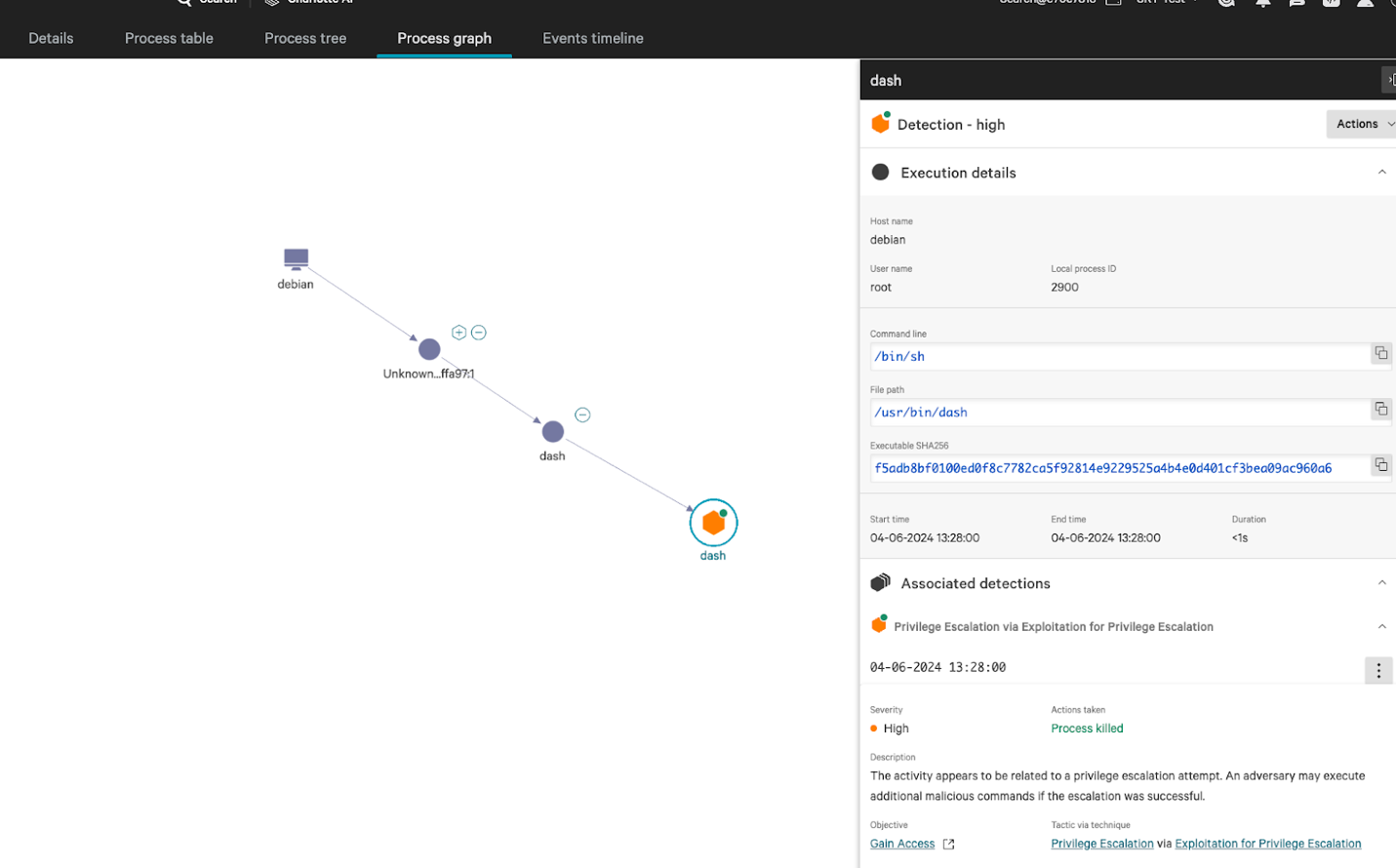
Figure 2. Exploit detection Process Graph view, with detailed view of Privilege Escalation prevented.
Conclusion and Recommendations
CrowdStrike continues to actively monitor this dynamic and ongoing situation. CrowdStrike will continue to take additional steps, including mitigation and patching, if new information becomes available. We will publish updates as necessary. In tandem, we continue to develop and release new behavioral logic for the Falcon platform to detect and prevent malicious behavior related to CVE-2024-1086.
We encourage customers to assess if their environment is running a vulnerable kernel version and apply the relevant patch following the Linux distribution guidelines
Relevant hash:
D1e32373f9a5dab0cc79f785f8533d784e06e3205243ab4e85123158f023abee
Additional Resources
- See how Falcon Exposure Management can help you discover and manage vulnerabilities and other exposures in your environments.
- Make prioritization painless and efficient. Watch how CrowdStrike Falcon® Spotlight enables IT staff to improve visibility with custom filters and team dashboards.
- Test CrowdStrike next-gen antivirus for yourself with a free trial of CrowdStrike® Falcon Prevent™.






![Helping Non-Security Stakeholders Understand ATT&CK in 10 Minutes or Less [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/video-ATTCK2-1?wid=530&hei=349&fmt=png-alpha&qlt=95,0&resMode=sharp2&op_usm=3.0,0.3,2,0)
![Qatar’s Commercial Bank Chooses CrowdStrike Falcon®: A Partnership Based on Trust [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/Edward-Gonam-Qatar-Blog2-1?wid=530&hei=349&fmt=png-alpha&qlt=95,0&resMode=sharp2&op_usm=3.0,0.3,2,0)