This blog was originally published on June 11, 2019.
As announced in our recent security advisory on CVE-2019-1040, Preempt (now CrowdStrike) researchers discovered how to bypass the MIC (Message Integrity Code) protection on NTLM authentication and modify any field in the NTLM message flow, including the signing requirement. This bypass allows attackers to relay authentication attempts which have negotiated signing to another server while entirely removing the signing requirement. All servers which do not enforce signing are vulnerable.
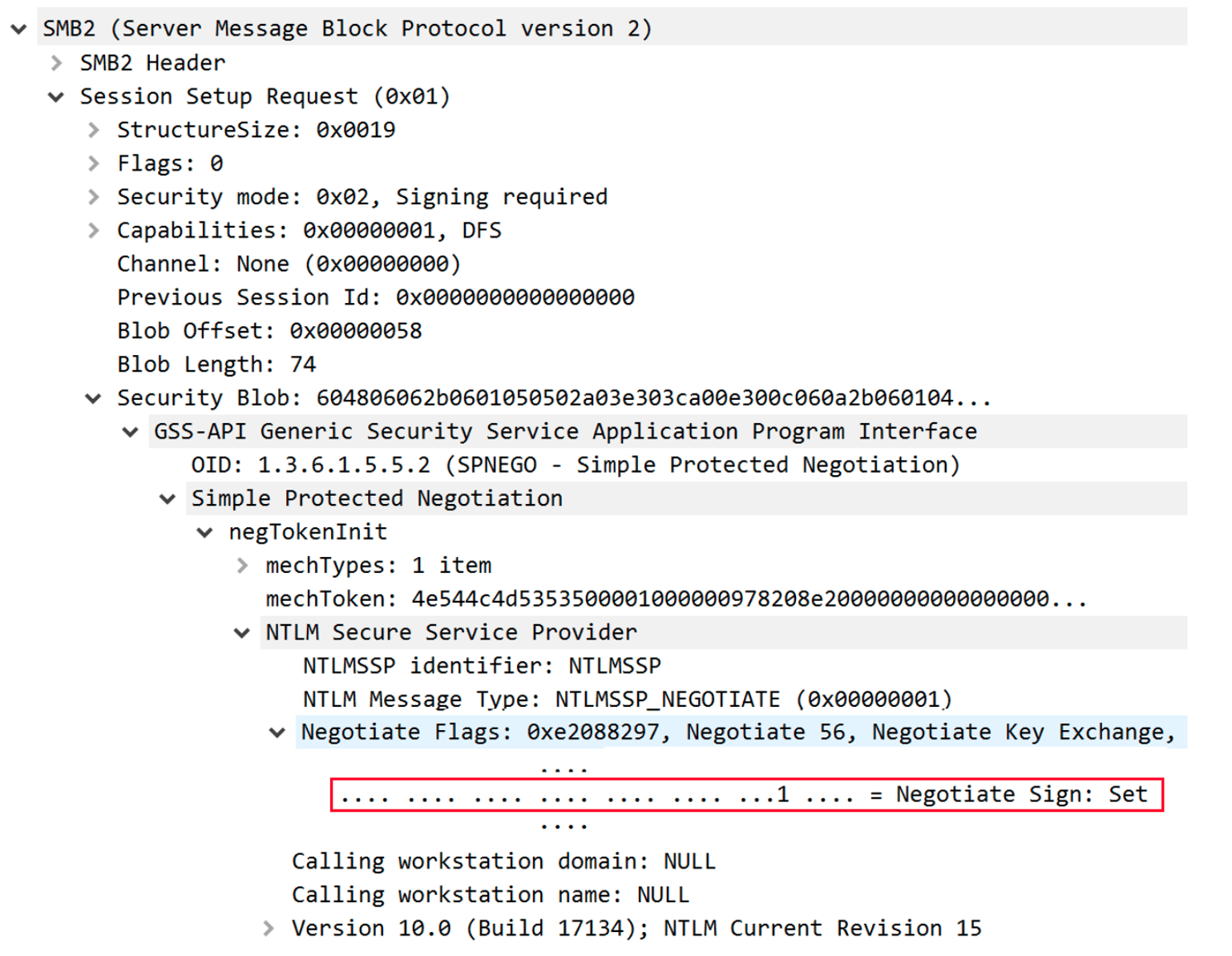
 Figure 3. The ‘flags’ field indicating that the NTLM_AUTHENTICATE message includes a MIC (Click to enlarge)
Figure 3. The ‘flags’ field indicating that the NTLM_AUTHENTICATE message includes a MIC (Click to enlarge)
CVE-2019-1040 Background
NTLM relay is one of the most prevalent attacks on Active Directory environments. The most significant mitigation against this attack technique is server signing. However, by default, only domain controllers enforce SMB signing, which in many cases leaves other sensitive servers vulnerable. However, in order to compromise such a server, attackers would need to capture an NTLM negotiation that does not negotiate signing, which is the case in HTTP but not in SMB, where by default if both parties support signing, the session would necessarily be signed. In order to ensure that the NTLM negotiation stage is not tampered with by attackers, Microsoft added an additional field in the final NTLM authentication message — the MIC. However, we discovered that until Microsoft’s latest security patch, this field was not effective.Session Signing
When users authenticate to a target via NTLM, they may be vulnerable to relay attacks. In order to protect servers from such attacks, Microsoft has introduced various mitigations, the most significant of which is session signing. When users establish a signed session against a server, attackers cannot hijack the session due to their inability to retrieve the required session key. In SMB, session signing is negotiated by setting the ‘NTLMSSP_NEGOTIATE_SIGN’ flag in the NTLM_NEGOTIATE message. The client behavior is determined by several group policies (‘Microsoft network client: Digitally sign communications’), for which the default configuration is to set the flag in question. If attackers attempt to relay such an NTLM authentication, they will need to ensure that signing is not negotiated. One way to do so is by relaying to protocols in which NTLM messages don’t govern the session integrity, such as LDAPS or HTTPS. The other is to modify the NTLM_NEGOTIATE message and unset the ‘NTLMSSP_NEGOTIATE_SIGN’ flag. However, in new NTLM versions, there is a protection against such modifications — the MIC field.MIC Overview
An NTLM authentication consists of 3 message types: NTLM_NEGOTIATE, NTLM_CHALLENGE, NTLM_AUTHENTICATE. To ensure that the messages were not manipulated in transit by a malicious actor, an additional MIC (Message Integrity Code) field has been added to the NTLM_AUTHENTICATE message. The MIC is an HMAC_MD5 applied to the concatenation of all 3 NTLM messages using the session key, which is known only to the account initiating the authentication and the target server. Hence, an attacker which tries to tamper with one of the messages (for example, modify the signing negotiation), would not be able to generate a corresponding MIC, which would cause the attack to fail. The presence of the MIC is announced in the ‘msvAvFlag’ field in the NTLM_AUTHENTICATE message (flag 0x2 indicates that the message includes a MIC) and it should fully protect servers from attackers which attempt to remove the MIC and perform NTLM relay. However, we found out that Microsoft servers do not take advantage of this protection mechanism and allow for unsigned (MIC-less) NTLM_AUTHENTICATE messages. Figure 3. The ‘flags’ field indicating that the NTLM_AUTHENTICATE message includes a MIC (Click to enlarge)
Figure 3. The ‘flags’ field indicating that the NTLM_AUTHENTICATE message includes a MIC (Click to enlarge)Drop the MIC
We discovered that all NTLM authentication requests are susceptible to relay attacks, no matter which protocol carries them. If the negotiation request includes a signing requirement, attackers would need to perform the following in order to overcome the protection of the MIC:- Unset the signing flags in the NTLM_NEGOTIATE message (NTLMSSP_NEGOTIATE_ALWAYS_SIGN, NTLMSSP_NEGOTIATE_SIGN)
- Remove the MIC from the NTLM_AUTHENTICATE message
- Remove the version field from the NTLM_AUTHENTICATE message (removing the MIC field without removing the version field would result in an error)
- Unset the following flags in the NTLM_AUTHENTICATE message: NTLMSSP_NEGOTIATE_ALWAYS_SIGN, NTLMSSP_NEGOTIATE_SIGN, NEGOTIATE_KEY_EXCHANGE, NEGOTIATE_VERSION




![Helping Non-Security Stakeholders Understand ATT&CK in 10 Minutes or Less [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/video-ATTCK2-1)
![Qatar’s Commercial Bank Chooses CrowdStrike Falcon®: A Partnership Based on Trust [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/Edward-Gonam-Qatar-Blog2-1)