Latin America (LATAM) is a growing market, and threat actors have used numerous eCrime malware variants to target users in this region. Over the past few years, many researchers have characterized the tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) of widespread Latin America malware families, including but not limited to Mispadu, Grandoreiro, Mekotio, Casbaneiro, Metamorfo and Astaroth.
According to our analysis, these malware families are primarily used to target Spanish- and Portuguese-speaking users of LATAM financial institutions. They also target Spanish- and Portuguese-speaking users from European countries and other parts of the world. These threats commonly implement language and geofencing filtering to avoid infecting users outside their scope.
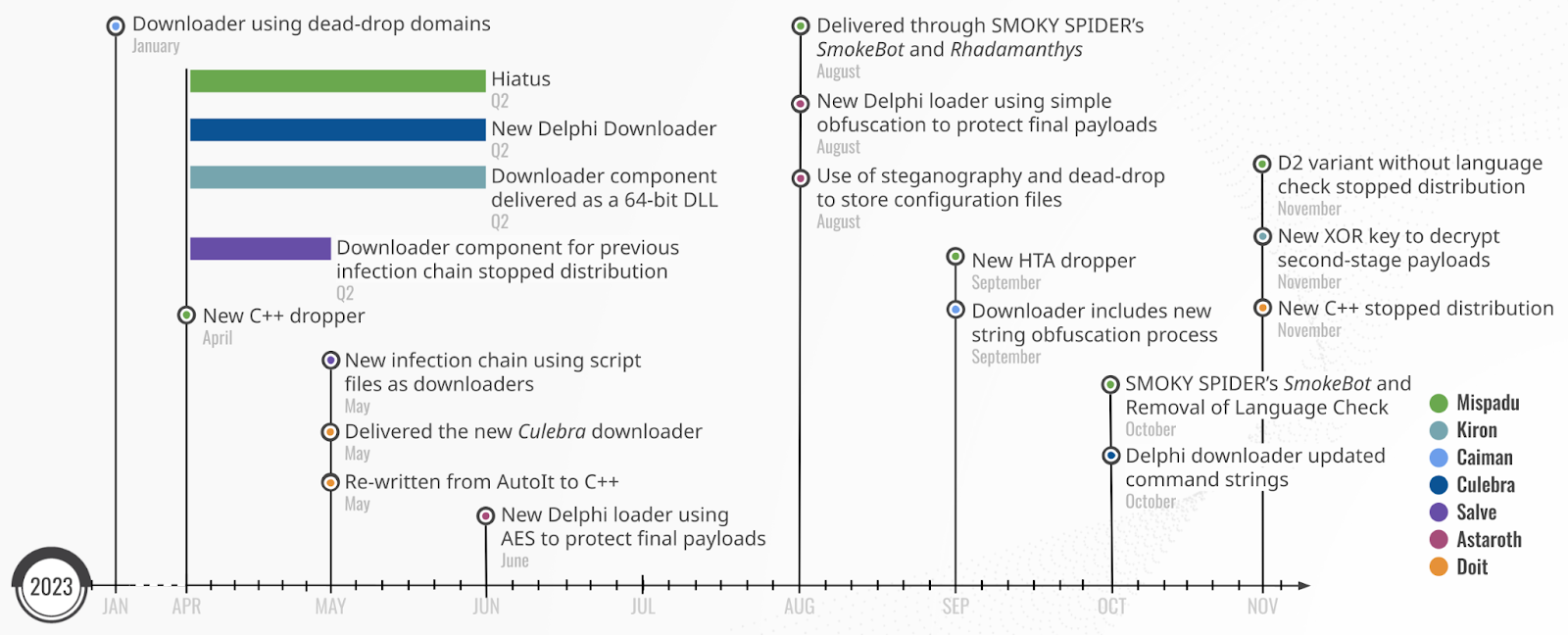
During 2023, these malware families were updated, focusing on improving defense evasion to stay competitive in the LATAM eCrime ecosystem. Among the updates, we found new components and obfuscation methods. This blog takes a closer look at these malware families, highlights these 2023 updates (Figure 1) and introduces the Brazilian-based adversary SAMBA SPIDER. Related indicators of compromise (IOCs) are attached at the end of this blog post, and a full list of IOCs is available in the CrowdStrike Intel Feed.
Common TTPs
Common TTPs for the threats detailed in this blog include:
- Multi-stage components: LATAM malware is composed of several stages intended to deliver a final payload that implements the core functionality. Each threat has at least two components: a downloader and a core payload.
- Implementation: LATAM malware developers prefer the Delphi programming language for core components; the downloader components are written in JScript or VBScript (VBS) but can also be written in Delphi.
- File inflation: Either the downloader or the core components are inflated to more than 100MB in size. This requires minimal effort but is an effective evasion technique, as some security solutions will not scan large files. Inflated components are delivered as compressed files and have a high compression ratio to download the component quickly.
- Packing: Either the Delphi downloader or core components can be heavily packed using VMProtect or Themida.
- Payload encryption: In some cases, core components are written to disk in an encrypted format, very likely to avoid host-based signatures. Encrypted payloads are decrypted at runtime and loaded in memory by a loader component.
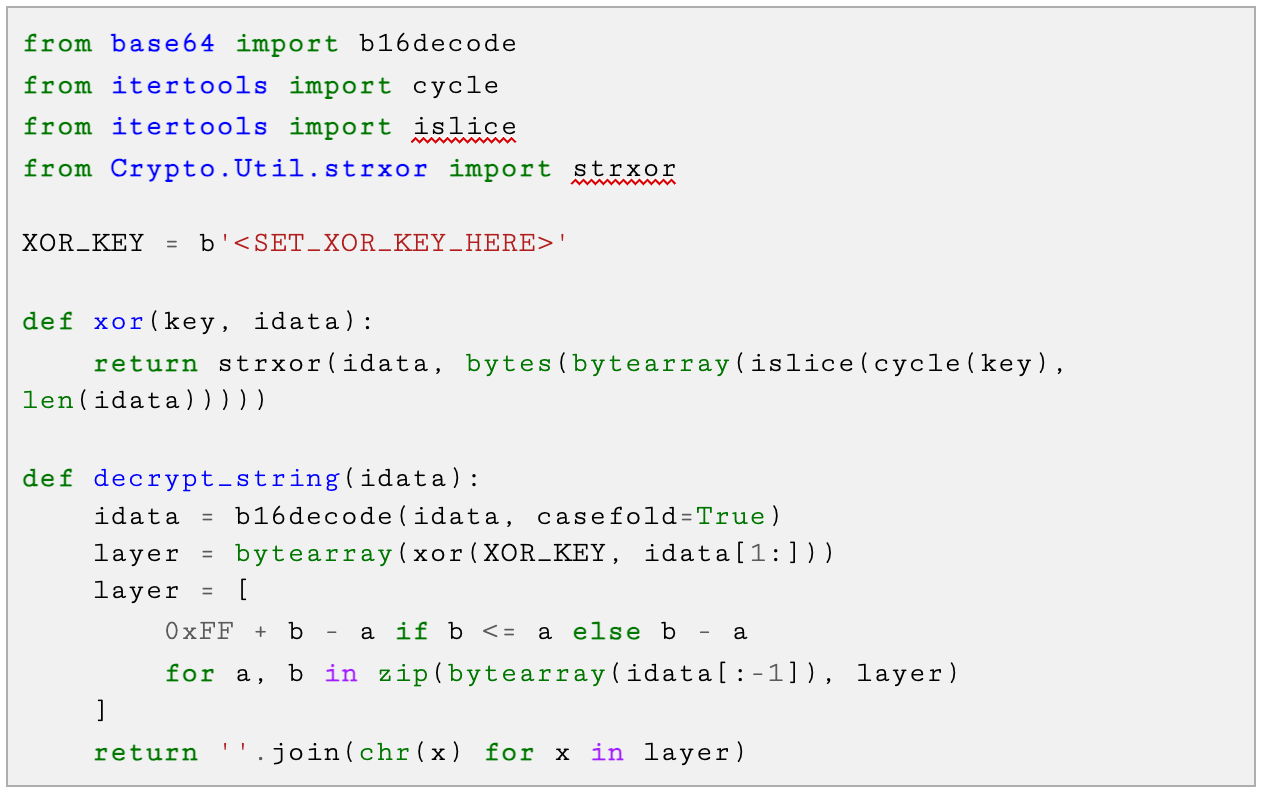
- String encryption: Most of the analyzed threats use the same XOR-based algorithm to encrypt strings as an anti-analysis technique to hinder static analysis. Depending on the malware family, additional layers of obfuscation have been implemented (the Python re-implementation for the XOR algorithm is attached in the Appendix).
- Filtering: Downloader components normally implement language filtering to avoid infecting non-Spanish-speaking and non-Portuguese-speaking users. Filters can be implemented not only at the host level by checking the system language but also at the network level by validating the system’s geolocation on the server side.
- Targeting: LATAM malware contains a list of hardcoded strings that identify targeted financial institutions (i.e., bank names). To harvest banking data, the malware loops over open windows (or inspects the foreground windows) to determine whether the window title contains a string from the hardcoded list. If found, the malware notifies the command-and-control (C2) server of the match.
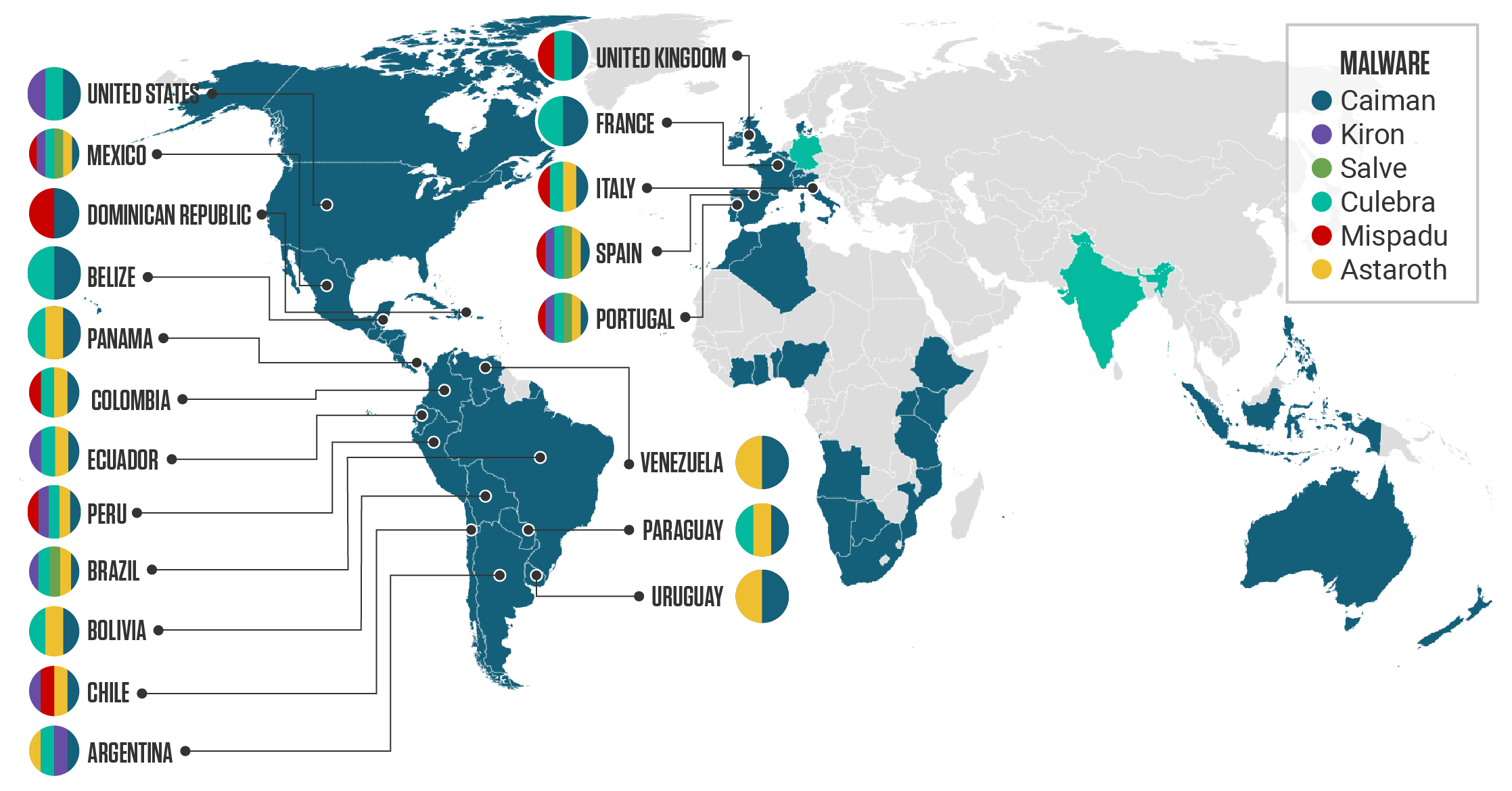
Targeted Countries
Figure 2 displays the countries targeted by each analyzed malware family. The map is based on extracted hardcoded strings that reference targeted financial institution names.
Mispadu: Introducing SAMBA SPIDER
SAMBA SPIDER is a Brazil-based threat actor that deploys the LATAM-developed malware Mispadu in financially motivated cyber operations. SAMBA SPIDER collects credentials using Mispadu’s information stealer functionality, which integrates NirSoft freeware tools to harvest data.
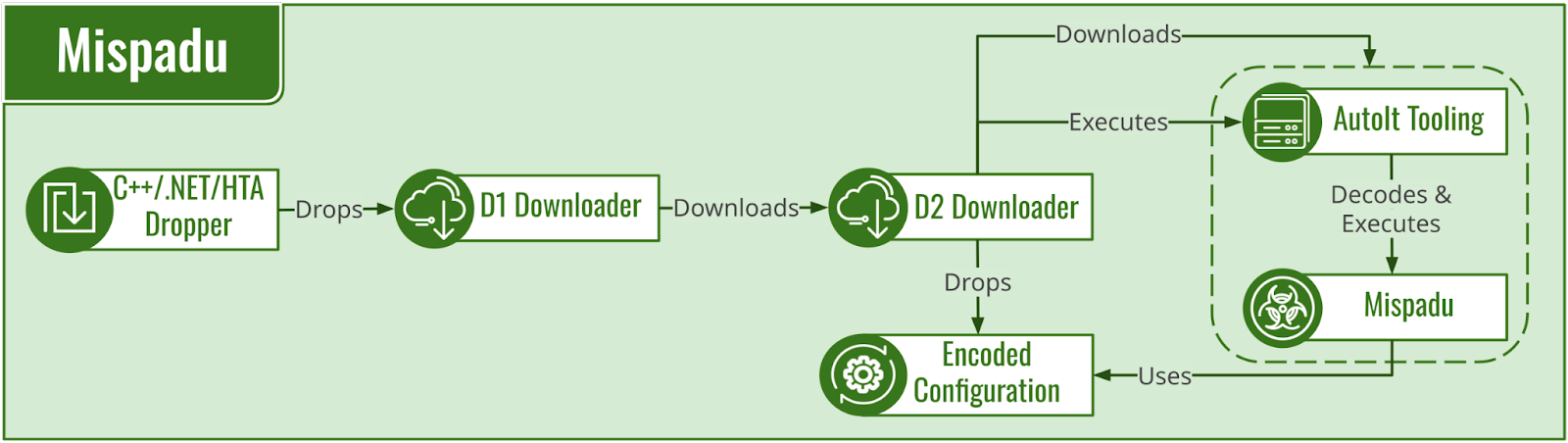
Mispadu — a banking trojan and information stealer that first appeared in 2019 — is delivered through a long infection chain composed of two VBS files (D1 and D2 downloaders). These files download and execute AutoIt tools that decode and execute Mispadu. The D2 downloader prevents undesirable infections by inspecting the system language (which must be Spanish or Portuguese) and implements virtual environment detection. The D2 downloader retrieves an AutoIt loader and an encoded Mispadu payload (Figure 3).
In 2023, the Mispadu deployment chain was updated and now delivers the VBS D1 downloader within C++ and HTA droppers. Additionally, malware activity appeared to pause between Q2 2023 and August 2023, during which most of the infrastructure went offline. The latest Mispadu version observed as of this writing is 96.
C++ Dropper
The C++ dropper, which was first observed in April 2023, implemented an anti-analysis technique that prompts the user to resolve a CAPTCHA challenge. This technique is also implemented in downloaders for other LATAM malware covered in this blog post. The CAPTCHA does not need to be resolved; when a user clicks any part of the CAPTCHA window, the dropper will continue execution.
The dropper runs a command line (Figure 4) that drops a VBS file — a Mispadu D1 downloader — to disk.
Two other dropper variants were also identified: another C++ variant that uses string obfuscation and a .NET variant. The C++ variant uses an algorithm dubbed E1 that encodes configuration files managed by the Mispadu D2 downloader. The .NET variant implements string obfuscation with AES-256 in CBC mode.
SMOKY SPIDER’s SmokeBot and Rhadamanthys
In August 2023, SMOKY SPIDER’s SmokeBot activity involving Rhadamanthys and Mispadu was identified. A Rhadamanthys sample was downloaded from a SmokeBot botnet that very likely served a Mispadu downloader. As the Rhadamanthys C2 server was no longer active at the time of analysis, directly observing Mispadu downloads and verifying the full infection chain was no longer possible.
HTA Dropper
In September 2023, a new dropper was implemented as an HTA file. This version drops the same obfuscated VBS downloader as the C++ version to disk. The HTA contains junk HTML code to increase the file size and implements two string obfuscation layers. This campaign distributed Mispadu version 94.
SMOKY SPIDER’s SmokeBot and Language Check Removal
In October 2023, SmokeBot directly delivered the C++ Mispadu dropper. Interestingly, the Mispadu D2 downloader did not implement a language check in this case, allowing the malware to infect systems configured for non-Spanish and non-Portuguese languages. This D2 variant stopped distribution in November 2023.
The Two Grandoreiros: Kiron and Caiman
Kiron (aka Grandoreiro) is likely one of the most active LATAM malware families, exhibiting a high volume of samples during 2023. Kiron is composed of two components: a downloader and a payload. The downloader retrieves an encrypted ZIP file that contains a Kiron payload (Figure 5).
Figure 6 contains a code snippet in Python that re-implements the Kiron decryption process to decrypt the downloaded ZIP files. Though the malware has historically used the XOR key 0x161a, it began using the key 0x19a9 in November 2023.
In Q2 2023, Kiron used 64-bit DLL downloaders; the malware previously only used 32-bit DLLs. Using 64-bit payloads is uncommon for this type of malware. In 2023, we also observed notable activity for another threat — which we track as Caiman (also referred to as Grandoreiro in public reporting) — distributed at a lower rate than Kiron (in terms of the number of samples).
Caiman vs. Kiron
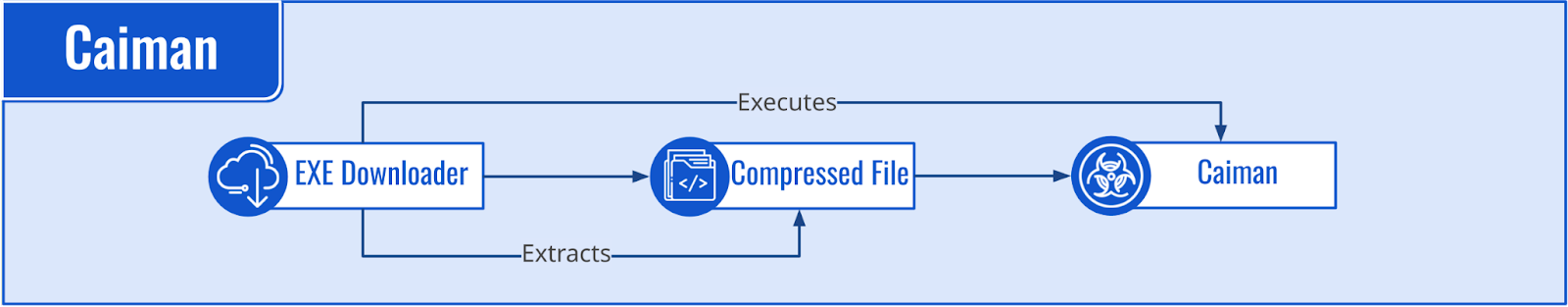
Kiron and Caiman implement a similar infection chain (Figures 5 and 7), delivering a compressed file that contains the malware payload. Kiron delivers ZIP files, and Caiman delivers compressed files starting with the magic number 61 5C 04 05 — which belongs to the WinHKI format — and are extracted using the Delphi library FlexCompress.1
The main difference between these threats is the downloader stage. The Kiron downloader simply queries a URL to retrieve a Kiron payload, whereas the Caiman downloader queries a dead drop to obtain a configuration containing a URL that hosts a Caiman payload.
Caiman downloaders implement filtering based on geolocation rather than system language.
Latenbot Kiron and Caiman have often been misclassified as Latenbot — a historical malware family — because Kiron, Caiman and Latenbot implement C2 protocols that are based on the open-source Delphi library Real Thin Client (RTC).2
Caiman Downloader: Dead Drops
In January 2023, Caiman downloader samples were configured to use a dead-drop domain to retrieve the final payload. To obtain the payload, the malware performs the following steps:
- Resolve the dead-drop domain to obtain the IP address.
- Calculate the destination port based on the IP. In this process, the malware deletes dots from the IP address and takes the four first numbers. It applies a substitution cipher in which each number is replaced with another number. This results in a new four-digit number that is used as the C2 port.
- The malware collects system information following the pattern from Figure 8.
- The information is encrypted with the reversed operation of the well-known XOR algorithm attached in the Appendix.
- The data is sent to the C2 server in an HTTP GET request.
- The response is an encrypted blob of data that can be decrypted using the same XOR-based algorithm.
An example of a decrypted configuration file is shown in Figure 9, which contains (among other fields) the Caiman download URL (ending in .xml) and the beacon URL (ending in .php). The beacon URL is queried to announce the infection to the C2 server.
This downloader also implements a CAPTCHA challenge as a measure to avoid running in sandboxes. Unlike Mispadu, the downloader will only continue execution if the CAPTCHA is resolved. The downloader can also inspect running processes to search for common analysis tools and therefore avoid dynamic inspection.
Caiman Downloader: Recent Updates
In September 2023, the Caiman downloader was updated to include new parameters in the collected system information (Figure 10). This includes the current date, the hard-disk volume ID and the country where the infected system is located. The country is obtained by querying the geolocation service ip-api<.>com.
In the new version, the Caiman downloader uses new values in the substitution cipher to calculate the C2 port. The downloader also includes more string encryption layers in addition to the XOR-based algorithm. The process to decrypt a string is detailed below. Table 1 contains an example of this process.
- The malware implements another substitution cipher that uses a hardcoded dictionary of characters containing a list of key-value pairs that the malware uses to decode the string.
- Caiman uses the aforementioned XOR-based algorithm to decrypt the result from Step 1. The XOR key is hardcoded in chunks that are concatenated at runtime.
- Step 2 produces a Base64-decoded string. The decoding results in a chunk of bytes used in Step 4.
- To obtain the raw string, Caiman uses AES-256 in CBC mode from the open-source library mORMot.3 Caiman uses a hardcoded and encrypted AES key and initialization vector (IV) that are decrypted with Steps 1 and 2. The result from Step 3 (the Base64-decoded data) is AES decrypted, obtaining the final result.
| Step | Encrypted String |
| 1 | WG%$U$CGPU)VTV*)U*%@G*GWXGTPTS%QUX,$TW%SVSW,S,,UTXW$GQVC@XV%PV$QXQQ),XT*WQS%%PG@*$V$,UU$*,XUQ*$TX$GX*%X*UV$@UC@,@P,)TTXTU*@G)SSS)GS*$%TTTC*GTUWW%PQT@PGUPS%TPP,TUT,*WGG@%)WQGTXCV@,)QUPTCT)C*SSC,VQ$*PVQV)$CWX)VT,G,%$QSP)@TWVX%WGG%SP$%T$WC)Q@VWQWXTQQ*PGQQCCCV*XS)@U |
| 2 | 23CF7F9387B414DB7DCA3D32031815C670EF12C5452E5EE7102F3649A04C84F6066BE01D265CC83ADF4FE77FDE076DF10F30DC0D74FA79AEA8EB11017DA3B555B35DFC1119D31722C861A83785C188E171ED233ACB2631094AEB678191B9D559E46FD8464BF920B41E3ECF658BA1240C233C58FC1F29B6A42620166D83669994D05BA7 |
| 3 | hvZ8mqrnvB3FE2mFEOvW7JDbSP6JznQY4igCQ+CM9aUpRSSJoeeHKFjC1AI2tZVFBxYGnNZiW7py\r\nQU5zHaPS+ebgDDb+6Lzw/8dnmzNKVXpl0bEAaUTu5mI55gKb9V08 |
| 4 | 86 F6 7C 9A AA E7 BC 1D C5 13 69 85 10 EB D6 EC 90 DB 48 FE 89 CE 74 18 E2 28 02 43 E0 8C F5 A5 29 45 24 89 A1 E7 87 28 58 C2 D4 02 36 B5 95 45 07 16 06 9C D6 62 5B BA 72 41 4E 73 1D A3 D2 F9 E6 E0 0C 36 FE E8 BC F0 FF C7 67 9B 33 4A 55 7A 65 D1 B1 00 69 44 EE E6 62 39 E6 02 9B F5 5D 3C |
| Result | bombafantastic.is-a-financialadvisor<.>com |
Table 1. Caiman string decryption process example
Culebra Remains Active
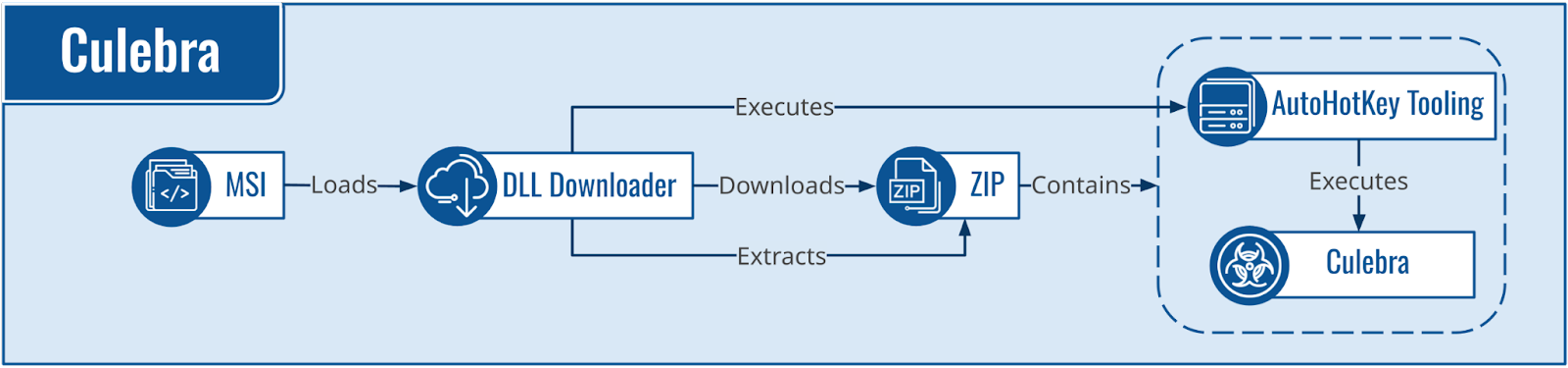
Culebra, publicly known as Mekotio and Metamorfo, has been active since 2017. Culebra samples are normally packed with Themida or VMProtect. This malware is delivered in a ZIP file that includes AutoHotKey4 tooling that loads the Culebra DLL payload.
During Q2 2023, an unidentified and high-prevalence Delphi-based downloader served the Culebra malware in all the observed instances. This Culebra downloader — which is also heavily packed — is delivered within Microsoft Installer (MSI) files (Figure 11).
Culebra Delphi-Based Downloader
Upon execution, the downloader queries the IPinfo<.>io service to obtain the infected system’s external IP address. Once obtained, the downloader concatenates the external IP address to the string pimbsbd and sends the result to the C2 server. If the C2 server replies with the string BSPCNFJBX, the connection has been filtered to avoid undesired traffic from IP addresses belonging to automated systems or users based in non-targeted countries. If an empty response is received, the malware sends the string ZPXJVRSB, which retrieves the next stage. The response is a blob of data that starts with the marker FQBPNQCF1 and contains a ZIP file with the Culebra malware and the AutoHotKey loader.
In October 2023, the downloader made a minor update using the string CFXSBPJBN as a response for bans and VYWMUSAE to request the next stage.
Salve
Salve is publicly known as Casbaneiro. This malware is notable due to its string obfuscation technique implemented in an early version that was not distributed from late Q1 2022.
Metamorfo Tag
Several LATAM banking trojans — such as Culebra and Salve — reuse the C2 protocol from the open-source tool Remote Access PC (RAPC).5 Culebra, Salve and other threats are therefore labeled as Metamorfo.
During our investigation, two relevant Metamorfo clusters were found: Salve (which was named based on the command stringSalveinfo) and Comome (which is a variant delivered through the spambot Horabot). The last cluster was named Comome since it always contains the domaincomoinstalar<.>mebetween the encrypted strings; the domain is not used but is always included.
In May 2023, the Salve deployment chain was completely overhauled to use script files rather than a Delphi-based downloader. The old Delphi downloader not only used binary inflation but also string obfuscation by splitting the string in chunks that are defined among useless code. This technique is also present in the new dropper, and strings are concatenated at runtime and mapped into a list. Each time a string is decrypted, a list is created, and the string to decrypt is extracted from the list by passing an index that indicates the string position in the list.
The new downloader component is implemented in two script stages (Figure 12). The infection chain starts with an inflated dropper (using extra null bytes) that implements a CAPTCHA, which attempts to prevent the downloader from running in a sandbox. The dropper checks whether it is running in a virtual environment and whether the system language is Spanish.
The dropper also implements string encryption using the widespread XOR-based algorithm (see Appendix) and the same XOR key 584HG4841U987IO9876LS21345K985126FGD4554Y21A87F9 used in previous Salve payloads.
The dropper writes a first-stage JScript downloader to disk that retrieves an additional component: an obfuscated second-stage JScript downloader. The second stage is another downloader that retrieves a ZIP file containing the final Salve components. The second stage queries legitimate URLs besides the download URL in an effort to hide the malicious traffic. The downloaded ZIP file contains a Salve payload configured to use a dead-drop URL that hosts the final C2 address.
Prior to these changes, the previous Salve infection chain used password-protected ZIP files to deliver the final components. Most of these ZIP files used the password HUHGIUG894893klbgKJHGFKJHfd873ukygKJHGflk__nfwuhreg during 2022.
The Devil Is Still Out There: Astaroth
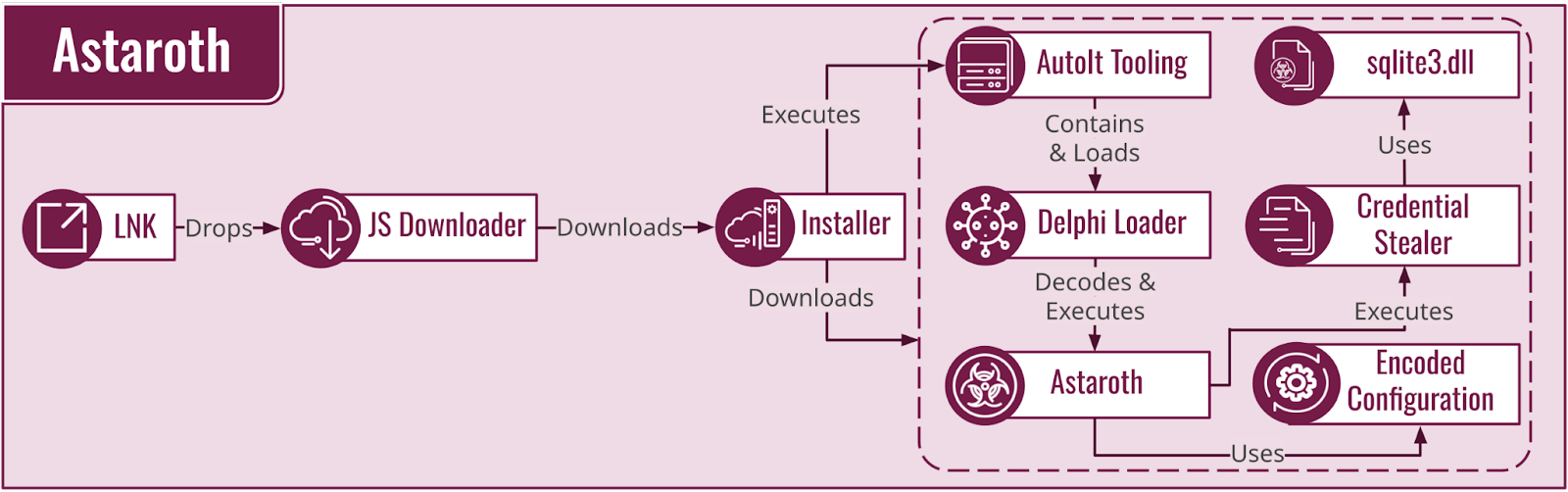
Astaroth (aka Guildma) — active since 2015 — is a banking trojan and information stealer that primarily targets users from LATAM, Spain, Italy and Australia. CrowdStrike Intelligence researched old Astaroth indicators and discovered a likely Brazil-based persona linked to the malware development.
Astaroth is delivered in a long deployment chain (Figure 13). The Astaroth downloader grabs an installer that retrieves other components: AutoIt tooling, a configuration file, an encrypted Astaroth payload, a copy of the legitimate sqlite3.dll and a credential stealer.
The Astaroth installer runs an AutoIt tool containing a Delphi loader that is executed in memory and was updated twice during 2023. Astaroth version 358 is the most current version as of this writing.
Astaroth Delphi Loader
In June 2023, the Astaroth deployment chain was updated to include a new Delphi loader. This component implements a code obfuscation technique that adds useless code to hide the actual functionality.
To decrypt the Astaroth payload, the new Delphi loader used AES in CTS mode from the open-source library DelphiEncryptionCompendium6 with a 24-byte key. The AES key is a hardcoded string with value x84 x115 x116 x111 x108 x97 x115 x118 x97 x114 x111 x114 x104 x97 x109 x105 x108 x115 x65, which is the decimal representation of each character prepended by an x. The key decodes to TstolasvarorhamilsA. Previous loader versions used a custom seeded-, shift- and XOR-based algorithm with a key that was calculated based on the position of the byte to decrypt.
In campaigns beginning in August 2023, the AutoIt components were briefly removed, and the Delphi loader was updated again. In these campaigns, the installer runs the loader using search-order hijacking with a legitimate Microsoft executable. However, Astaroth moved back to the AutoIt script where the Delphi loader is contained. In this version, the Delphi loader implements a new algorithm that uses a byte subtraction operation to decode the Astaroth payload.
Steganography and Dead Drops
In August 2023, Astaroth began to use steganography and dead-drop URLs that host configuration files. The dead-drop URLs download image files that contain an encoded configuration between the markers #0=.#3 and #0=.#9.
The Connection: Mispadu and Astaroth Our analysis uncovered several overlaps between Mispadu and Astaroth, suggesting that the same developer likely either created both malware families or reused techniques from the same source. This assessment is made with moderate confidence based on the following factors:As of this writing, whether the Mispadu and Astaroth developer(s) are the same persona, are part of the same group or have another relationship that might explain these overlaps is unknown.
- Astaroth protects C2 communications with the same encoding algorithm (E1) that Mispadu uses to protect configurations
- The script code used in the downloader for both threats implement the same obfuscation
- Both use a similar AutoIt loader to execute the final payload
- Mispadu and Astaroth payloads remain encrypted in disk and are only decrypted to be loaded in memory
- Deployment chains are similar (see Figures 3 and 13)
Bonus: Doit
From September 2022 and throughout 2023, we observed a high-prevalence threat that implements stealer and downloader functionalities that served Mispadu in late 2022 and Culebra in May 2023. Industry sources classified this threat as Mispadu; however, according to our analysis, this new threat works differently. It was named Doit because it always uses the same URL path: do/it.php.
CrowdStrike Intelligence recovered thousands of credentials from the Doit botnet belonging to users from Peru, Chile and Mexico, including credentials for government institutions.
Notably, aside from the downloader and stealer functionality, Doit can install Google Chrome enrollment tokens, which would permit a criminal actor to remotely control a Google Chrome instance to install malicious extensions.
In May 2023, the malware was rewritten to C++, and the downloader and stealer functionalities were removed. The malware only maintained the Google Chrome enrollment process and the ability to modify Microsoft Edge policies (by modifying the system registry), likely to silently install browser extensions. This new version only targets Mexico-based users, as it includes a filter to determine whether the malware is running in a system located in a time zone between UTC-5 to UTC-8, which is the Mexico area. The Doit C++ stopped distribution in November 2023.
Conclusion
The various 2023 updates to Mispadu, Kiron, Caiman, Culebra, Salve and Astaroth indicate that these malware families are still active in the region and targeting users from several countries, even outside of LATAM.
Over the years, developers have retooled these threats in an attempt to improve their defense evasion. The most notable changes during 2023 are the use of CAPTCHAs, new components in the infection chain and new obfuscation methods. For example, several LATAM threats implemented CAPTCHAs, which suggests the developers are exchanging knowledge. This is not the only shared technique, and other overlaps are present in several threats as well (see the Common TTPs section).
Based on historical analysis and the activities described in this blog, these threat actors will very likely implement new techniques focused on improving evasion during 2024.
Recommendations
To avoid or detect eCrime commodity malware infections, CrowdStrike CAO recommends the following:
- Be wary of emails from untrusted sources that expect the user to execute unknown files
- Ensure downloaded software originates from a legitimate source by checking the website’s certificates on the download page
- Use browser settings that enable download protection and can issue warnings about potentially harmful websites or downloads
Indicators of Compromise
| Malware | Description | Indicator |
| Mispadu | SHA256 C++ dropper non-obfuscated version | dbb2e294a65eb3fa1bbe1a25c2baf352a01250d567cfa953d4f942c2b5f08e53 |
| SHA256 C++ dropper obfuscated version | d56863d940d5ccd1922bbbdf65471c493701e3b10be5c522851c8efbdaeb9fae | |
| SHA256 .NET dropper | ac97f893f8243db3c5ccfbc89d83b97534c1b73d0289ccb61bfb2c035f539126 | |
| SHA256 HTA dropper | f873062ff206ad60cb4b790c2ba83624c510f15dbc4905d5c96668f87999c16a | |
| SHA256 D2 downloader | 7b6444e5be24ce95cdcac357cf20ddc77abda142a16202ab3677b7d29a1e0da3 | |
| SHA256 payload version 96 | 78e3e51ddeac0519d434a8b192bae61bbaa278154a9511676c8a58079d95beb5 | |
| SmokeBot download URL that served Mispadu | http<:>//84.54.50<.>102/FX_432661.exe | |
| SmokeBot download URL that served a Rhadamanthys payload connected to Mispadu | http<:>//amx55<.>xyz/rh111.exe | |
| Kiron | SHA256 downloader | a302c7bb7fdd8ca6c814bafa363953e12e05082c913d50085df8bb2d8d8cec88 |
| Download URL | http<:>//104.225.129<.>140:7738/hwnsjws.zip | |
| SHA256 payload | 4e05109d53396162d3e8e1c7730e9f9ccd31042440cfd3b143fa4b9441b8a638 | |
| Caiman | SHA256 downloader from January 2023 | 5f90ff7355d210a96eacb5e563d0d72b33ab57f218ba2e3e9171a83f2dc7f45a |
| SHA256 downloader from September 2023 | 916e31e3465f68bdfd4228cb12f3ce00414957cb391c97e5ec7cdb0d9ca29b4a | |
| Dead-drop domain | cozineros.merseine<.>com | |
| Dead-drop IP address | 35.175.173<.>110 | |
| Download URL | http<:>//35.175.173<.>110:28557/cexjBNIai.xml | |
| Culebra | SHA256 downloader | 5a014547017b3d7d4c0e2b65bc6be68a076032ceb99a344e459cbd4469e67e90 |
| SHA256 payload | dfac705145ec8a879cac1517411910e4305aab160cc6627d5becbaa7edf8c7af | |
| Salve | SHA256 previous inflated PE downloader | 8ca790031ec97e768abb9978b33bba714e0c00ac76c80f93497549cad989a225 |
| SHA256 dropper | 78c3695f33064589755bdd270f99ca7417e5e74e3a14ee58cd4e71ce050a16a6 | |
| First-stage JScript C2 | storage-cloudbr<.>com | |
| Second-stage JScript download URL | https<:>//s-ed1.cloud.gcore<.>lu/240723/completar.online | |
| Dead-drop URL for payload | https<:>//snippets.cacher<.>io/snippet/aca4e5621c0ba9b5ff90 | |
| Payload C2 IP | 191.55.63<.>128 | |
| Astaroth | Compiled AutoIt script that contains a Delphi loader using AES | 8443bed542bdb358a7a5303b93e9489ac9c09bd80869ed880bea1b23cb48b860 |
| Latest Delphi DLL loader | a88028f6834e209b475b96b082c53925a7d11fa9bc65b47a56c54a658d1bd970 | |
| PNG file hiding a configuration file | f16b05958e590adcdc6be5d45df93d4f5405be2182d8ad4ba749d7c037890a0e | |
| Doit | AutoIt version | eba4055047dceb89399a64c0448e30186b90196870dbcb209809592be05750c5 |
| C++ version | 5292cc96a84c885f10ceb10993183bcb8b43b1079867d46e596c8b6e2cdb86f8 | |
| C2 server hosting Mispadu | https<:>//documents.drive.dreamixcorporation<.>com/do/it.php | |
| C2 server hosting Mispadu | http<:>//highlineadsl<.>com/ddd/it.php | |
| URL hosting a Culebra downloader | https<:>//www.dropbox<.>com/s/br44jhgw5qfseqm/Mfsmc5LU.msi?dl=1 |
Appendix: XOR-Based String Decryption Algorithm
Additional Resources
- Learn more about adversaries that may be targeting your region or industry in the CrowdStrike Adversary Universe.
- Who are today's threat actors? What are they after? And most importantly, how can you defend against them? Listen to the Adversary Universe podcast, where CrowdStrike answers all of these questions — and more.
- Learn about our threat intelligence and hunting subscriptions.
- Experience how the industry-leading CrowdStrike Falcon® platform protects against modern threats. Start your 15-day free trial today.
- https<:>//www.componentace<.>com/compression_component_compression_delphi_encryption_delphi_flexcompress.htm
- https<:>//github<.>com/teppicom/RealThinClient-SDK
- https<:>//github<.>com/synopse/mORMot
- https<:>//www.autohotkey<.>com/
- https<:>//github<.>com/abalad/Delphi_Remote_Access_PC
- https<:>//github<.>com/MHumm/DelphiEncryptionCompendium






![Helping Non-Security Stakeholders Understand ATT&CK in 10 Minutes or Less [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/video-ATTCK2-1?wid=530&hei=349&fmt=png-alpha&qlt=95,0&resMode=sharp2&op_usm=3.0,0.3,2,0)
![Qatar’s Commercial Bank Chooses CrowdStrike Falcon®: A Partnership Based on Trust [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/Edward-Gonam-Qatar-Blog2-1?wid=530&hei=349&fmt=png-alpha&qlt=95,0&resMode=sharp2&op_usm=3.0,0.3,2,0)