Microsoft has released security updates for 34 vulnerabilities, including one previously disclosed zero-day (CVE-2023-20588), a vulnerability affecting Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) processors. Four of the vulnerabilities addressed today are rated as Critical while the remaining 30 are rated as Important.
December 2023 Risk Analysis
This month’s leading risk type is elevation of privilege (29%), followed by remote code execution (23%) and information disclosure (18%).
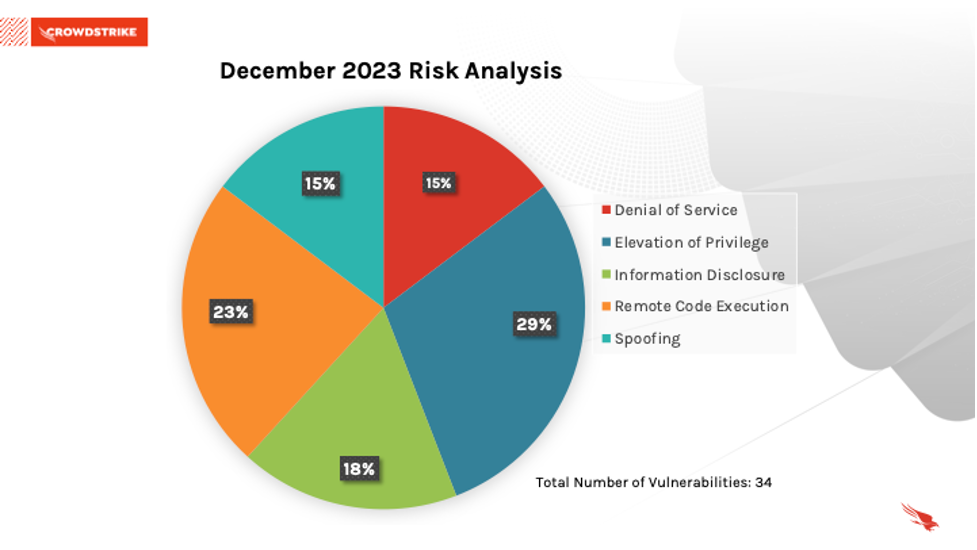 Figure 1. Breakdown of December 2023 Patch Tuesday attack types
Figure 1. Breakdown of December 2023 Patch Tuesday attack types
The Microsoft ESU product family received the most patches this month with 18, followed by Windows (7), and a tie between Azure (3) and Office (3).
 Figure 2. Breakdown of product families affected by December 2023 Patch Tuesday
Figure 2. Breakdown of product families affected by December 2023 Patch Tuesday
Previously Disclosed Zero-Day Vulnerability Affects AMD Processors
AMD CPUs have received a patch for CVE-2023-20588, which is rated Important and has a CVSS score of 5.5. This is a division-by-zero error on some AMD processors that can potentially return speculative data resulting in loss of confidentiality. Prior to the fix released today, AMD offered mitigations for this vulnerability back in August 2023. The proof of concept has already been publicly disclosed.
| Severity | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Important | 5.5 | CVE-2023-20588 | AMD: CVE-2023-20588 AMD Speculative Leaks Security Notice |
Table 1. Zero-day in AMD processors
Critical Vulnerabilities Affect Microsoft Windows, ESU, Dynamics and Azure
CVE-2023-35628 is a Critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting Microsoft Windows MSHTML (Microsoft Hypertext Mark-up Language) platform with a CVSS score of 8.1. An attacker would have to send a specially crafted email for the vulnerability to automatically trigger after the Outlook client has received and processed the message. This would allow the exploitation to happen before the email is viewed. The attack complexity is high due to relying on complex memory-shaping techniques in order to successfully exploit the vulnerability.
CVE-2023-35630 and CVE-2023-35641 are Critical RCE vulnerabilities affecting Microsoft Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) with a CVSS score of 8.8. Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities relies on the host being connected to the same network segment as an attacker. These vulnerabilities cannot be exploited across multiple networks. Even though the complexity of this attack is low, it is limited to a particular environment for the exploit to be successful.
CVE-2023-36019 is a Critical spoofing vulnerability affecting Microsoft Power Platform Connector with a CVSS score of 9.6. Successful exploitation of this vulnerability relies on the user clicking on a specially crafted URL. This vulnerability is in the web server; however, the malicious scripts execute on the victim’s browser. Microsoft addressed this vulnerability by making newly created custom connectors that use OAuth 2.0 to authenticate automatically with a per connector redirect URI. Microsoft urges customers to update existing OAuth 2.0 connectors to use a per connector redirect URI.
| Severity | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Critical | 9.6 | CVE-2023-36019 | Microsoft Power Platform Connector Spoofing Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.8 | CVE-2023-35630 | Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.8 | CVE-2023-35641 | Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.1 | CVE-2023-35628 | Windows MSHTML Platform Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Table 2. Critical vulnerabilities in Windows, ESU, Dynamics and Azure
Not All Relevant Vulnerabilities Have Patches: Consider Mitigation Strategies
As we have learned with other notable vulnerabilities, such as Log4j, not every highly exploitable vulnerability can be easily patched — as is also the case for the ProxyNotShell vulnerabilities. It’s critically important to develop a response plan for how to defend your environments when no patching protocol exists.
Regular review of your patching strategy should still be a part of your program, but you should also look more holistically at your organization's methods for cybersecurity and improve your overall security posture.
The CrowdStrike Falcon® platform regularly collects and analyzes trillions of endpoint events every day from millions of sensors deployed across 176 countries. Watch this demo to see the Falcon platform in action.
Learn More
Learn more about how CrowdStrike Falcon® Spotlight can help you quickly and easily discover and prioritize vulnerabilities here.
About CVSS Scores
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a free and open industry standard that CrowdStrike and many other cybersecurity organizations use to assess and communicate software vulnerabilities’ severity and characteristics. The CVSS Base Score ranges from 0.0 to 10.0, and the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) adds a severity rating for CVSS scores. Learn more about vulnerability scoring in this article.
Additional Resources
- For more information on which products are in Microsoft’s Extended Security Updates program, refer to the vendor guidance here.
- Make prioritization painless and efficient. Watch how Falcon Spotlight enables IT staff to improve visibility with custom filters and team dashboards.
- Download the CrowdStrike 2023 Global Threat Report and CrowdStrike 2023 Threat Hunting Report to learn how the threat landscape has shifted in the past year and understand the adversary behavior driving these shifts.
- See how CrowdStrike Falcon® Spotlight vulnerability management can help you discover and manage vulnerabilities and prioritize patches in your environments.
- Test CrowdStrike next-gen AV for yourself with a free trial of CrowdStrike Falcon® Prevent next-generation antivirus.




![Helping Non-Security Stakeholders Understand ATT&CK in 10 Minutes or Less [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/video-ATTCK2-1)
![Qatar’s Commercial Bank Chooses CrowdStrike Falcon®: A Partnership Based on Trust [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/Edward-Gonam-Qatar-Blog2-1)











































