The first Patch Tuesday of 2023 is starting the year with a large number of bug fixes. Microsoft released 98 security patches for its January 2023 Patch Tuesday rollout, almost double the number released in December 2022. Eleven of these vulnerabilities are rated Critical including two zero-days, with one under active attack. The rest are rated Important.
The two zero-day vulnerabilities include a Windows Workstation Service Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability (CVE-2023-21549) that is listed as publicly known. The second zero-day, a Windows Advanced Local Procedure Call (ALPC) Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability (CVE-2023-21674), is listed as actively exploited at the time of release. The latter vulnerability has a CVSS of 8.8. This bug could allow a local attacker to escalate privileges from sandboxed execution inside Chromium to kernel-level execution and full SYSTEM privileges.
January 2023 Risk Analysis
This month’s leading risk type is elevation of privilege at 40%, an almost 10% increase compared with the December 2022 Patch Tuesday release, followed by remote code execution at 33% (down from 47% last month). The remaining categories each make up around 10% or less.
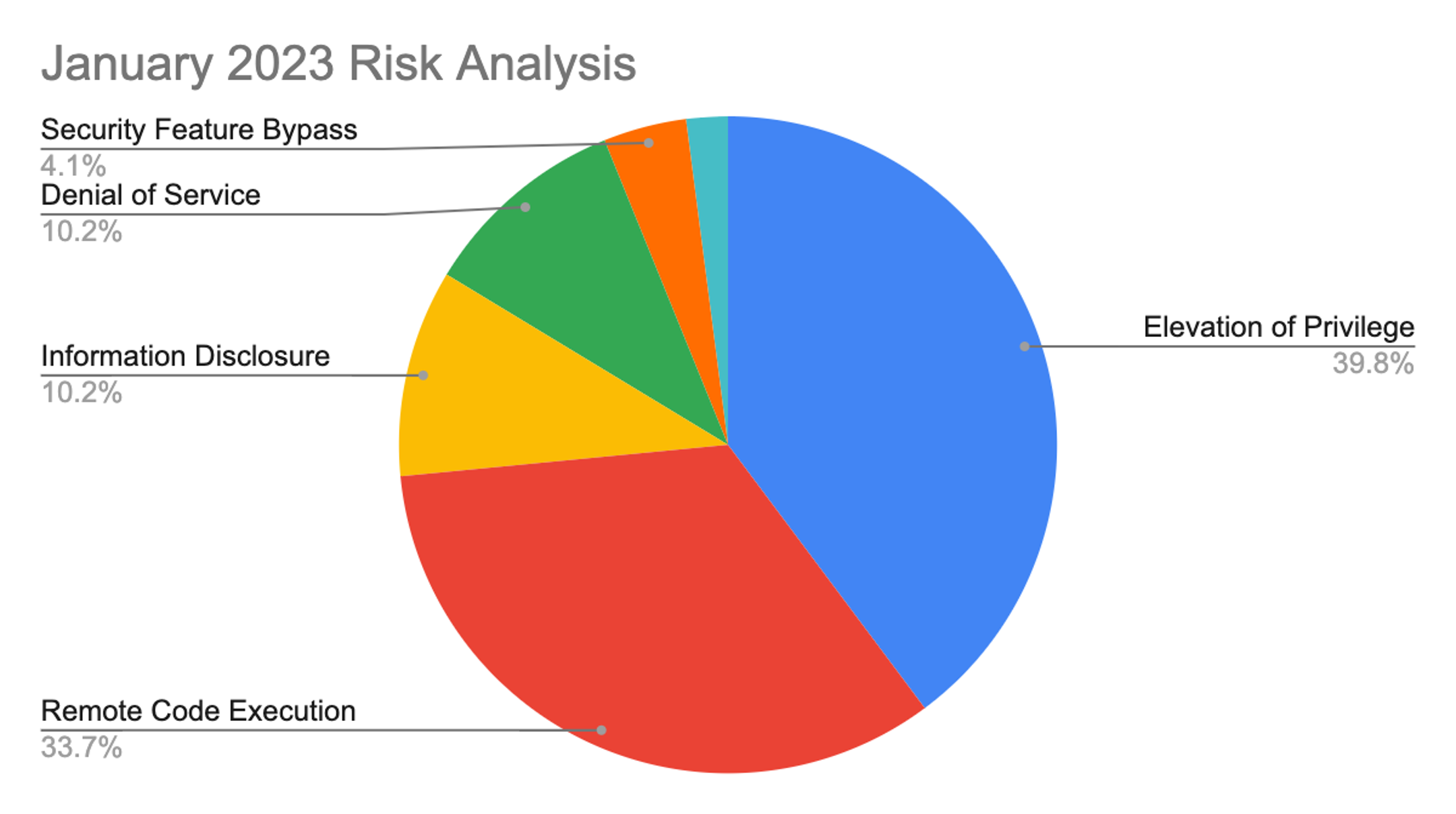 Figure 1. Breakdown of January 2023 Patch Tuesday attack types
Figure 1. Breakdown of January 2023 Patch Tuesday attack typesThe Microsoft Windows product family received the most patches this month (66), followed by Extended Support Updates (43) and Microsoft apps (14).
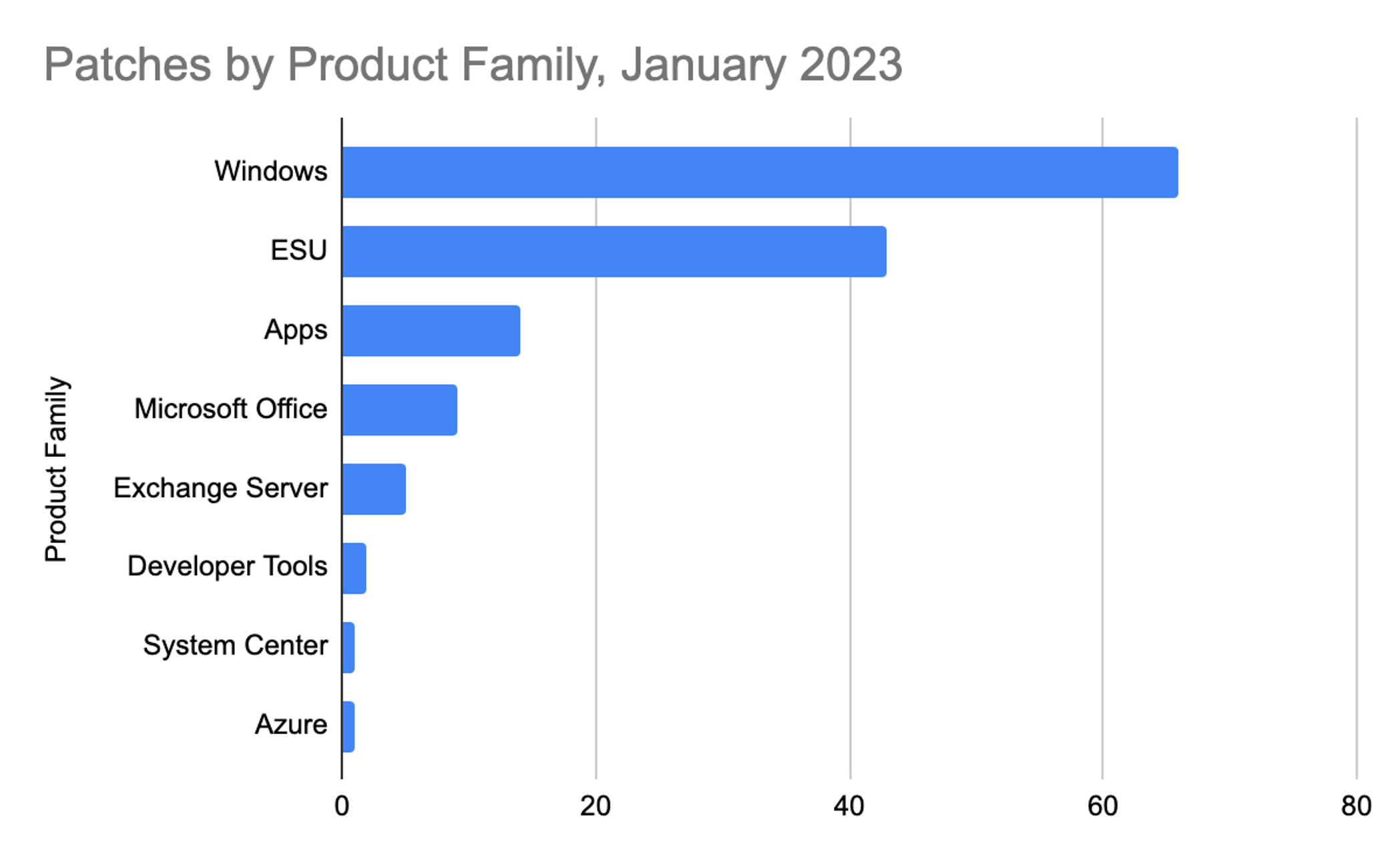 Figure 2. Breakdown of product families included in January 2023 Patch Tuesday
Figure 2. Breakdown of product families included in January 2023 Patch TuesdaySee for yourself how the industry-leading CrowdStrike Falcon platform protects against modern threats. Start your 15-day free trial today.
Critical Bugs Affect Windows Cryptographic Services, SSTP and L2TP
In this month's release, 11 Critical vulnerabilities are getting patched. The CVE-2023-21561 bug affects Microsoft Cryptographic Services and has a CVSS of 8.8. A locally authenticated attacker could send specially crafted data to the local CSRSS service to elevate their privileges from AppContainer to SYSTEM.
The Microsoft SharePoint Server Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability (CVE-2023-21743) could allow a remote, unauthenticated attacker to make an anonymous connection to an affected SharePoint server. Keep in mind that to fully remediate this vulnerability, you must also trigger a SharePoint upgrade action. The upgrade action can be triggered by running the SharePoint Products Configuration Wizard, the Upgrade-SPFarm PowerShell cmdlet, or the "psconfig.exe -cmd upgrade -inplace b2b" command on each SharePoint server after installing the update.
As shown in Figure 3, five bugs affect Windows Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP), all rated Critical with a CVSS of 8.1. According to Microsoft, an unauthenticated attacker could send a specially crafted connection request to a RAS server, which could lead to remote code execution (RCE) on the RAS server machine.
| Rank | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Critical | 8.8 | CVE-2023-21561 | Microsoft Cryptographic Services Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.2 | CVE-2023-21743 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.1 | CVE-2023-21543 | Windows Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.1 | CVE-2023-21546 | Windows Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.1 | CVE-2023-21555 | Windows Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.1 | CVE-2023-21556 | Windows Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.1 | CVE-2023-21679 | Windows Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.1 | CVE-2023-21535 | Windows Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.1 | CVE-2023-21548 | Windows Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 7.8 | CVE-2023-21551 | Microsoft Cryptographic Services Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Critical | 7.8 | CVE-2023-21730 | Windows Cryptographic Services Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Figure 3. Critical vulnerabilities in SSTP, L2TP and Windows Cryptographic Services
Important Microsoft Exchange Server Vulnerabilities
Also addressed this month are CVE-2023-21762 and CVE-2023-21745, two spoofing vulnerabilities affecting Exchange Server, both with a CVSS of 8. If successfully exploited, CVE-2023-21762 could lead to NTLM hashes being exposed, while CVE-2023-21745 could allow an authenticated attacker to achieve exploitation given a PowerShell remoting session to the server.
Moving on to the privilege escalation bugs, CVE-2023-21763 and CVE-2023-21764 could allow an attacker to load their own DLL and execute code at the level of SYSTEM. Keep in mind that the attack vector is listed as Local, and User interaction is not required. Both vulnerabilities are rated with a CVSS of 7.8. As usual, we highly recommend taking action on these vulnerabilities, especially if you have on-premises versions.
| Rank | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Important | 8 | CVE-2023-21762 | Microsoft Exchange Server Spoofing Vulnerability |
| Important | 8 | CVE-2023-21745 | Microsoft Exchange Server Spoofing Vulnerability |
| Important | 7.8 | CVE-2023-21764 | Microsoft Exchange Server Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important | 7.8 | CVE-2023-21763 | Microsoft Exchange Server Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important | 7.5 | CVE-2023-21761 | Microsoft Exchange Server Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
Figure 4. Microsoft Exchange Server vulnerabilities
Windows Credential Manager User Interface Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2023-21726, an Important vulnerability with a 7.8 CVSS getting patched this month, affects Windows Credential Manager User Interface. It requires no user interaction and could allow an attacker to gain SYSTEM privileges if successfully exploited.
As shown in Figure 5, we see once again more Print Spooler vulnerabilities fixed in this month's release. Two of these have a CVSS of 7.8 and a third bug has a CVSS of 7.1. Please consider prioritizing all of these vulnerabilities.
| Rank | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Important | 7.8 | CVE-2023-21726 | Windows Credential Manager User Interface Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important | 7.8 | CVE-2023-21678 | Windows Print Spooler Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important | 7.8 | CVE-2023-21765 | Windows Print Spooler Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important | 7.1 | CVE-2023-21760 | Windows Print Spooler Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
Figure 5. Windows Credential Manager User Interface Elevation of Privilege vulnerability
End of Support for Windows 8.1
According to a recent Microsoft publication, Windows 8.1 reached the end of support on January 10, 2023. After this date, this product will no longer receive security updates, non-security updates, bug fixes, technical support or online technical content updates. Rest assured, CrowdStrike will continue to support Windows 8.1, but we highly recommend you update your hosts running Windows 8.1 to a supported Windows version before July 9, 2023. Refer to our Falcon Sensor for Windows deployment guide or our Support Portal for all supported Windows versions.
Learn More
This video on CrowdStrike Falcon® Spotlight vulnerability management shows how you can quickly monitor and prioritize vulnerabilities within the systems and applications in your organization.
About CVSS Scores
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a free and open industry standard that CrowdStrike and many other cybersecurity organizations use to assess and communicate software vulnerabilities’ severity and characteristics. The CVSS Base Score ranges from 0.0 to 10.0, and the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) adds a severity rating for CVSS scores. Learn more about vulnerability scoring in this article.
Additional Resources
- Download the CrowdStrike 2022 Falcon OverWatch Threat Hunting Report to learn more about recent adversary tradecraft and tooling and get actionable tips for staying ahead of today's stealthiest, most sophisticated cyber threats.
- See how Falcon Spotlight can help you discover and manage vulnerabilities in your environments.
- Learn how Falcon identity protection products can stop workforce identity threats faster.
- Learn how the new External Attack Surface Module, Falcon Surface (EASM) can discover unknown, exposed and vulnerable internet-facing assets enabling security teams to stop adversaries in their tracks.
- Make prioritization painless and efficient. Watch how Falcon Spotlight enables IT staff to improve visibility with custom filters and team dashboards.
- Test CrowdStrike next-gen AV for yourself with a free trial of CrowdStrike Falcon® Prevent.






![Helping Non-Security Stakeholders Understand ATT&CK in 10 Minutes or Less [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/video-ATTCK2-1?wid=530&hei=349&fmt=png-alpha&qlt=95,0&resMode=sharp2&op_usm=3.0,0.3,2,0)
![Qatar’s Commercial Bank Chooses CrowdStrike Falcon®: A Partnership Based on Trust [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/Edward-Gonam-Qatar-Blog2-1?wid=530&hei=349&fmt=png-alpha&qlt=95,0&resMode=sharp2&op_usm=3.0,0.3,2,0)





















































