This month’s patch update covers 50 vulnerabilities, with 6 of them actively exploited - the highest number we’ve seen so far in 2021. Five of these in-the-wild exploits affect default Windows components, and one is a zero-day targeting MSHTML. All of them should be reviewed and prioritized quickly to protect against an attack.
Also of note: Due to the severity of one of the in-the-wild threats, Microsoft pushed out a cumulative out-of-band update for CVE-2021-33741 on June 4 (right before this month’s Patch Tuesday release). This vulnerability uses the Internet Explorer HTML engine to execute commands on affected systems and could occur within any application using MSHTML to render HTML content. We’ve included this CVE in our vulnerability review this month under “Other Important Vulnerabilities to Consider,” as this update was released last week. With the multiple active exploits for Windows, extra consideration should be given to expediting patching on these systems. Let’s get started.
New Patches for 50 Vulnerabilities
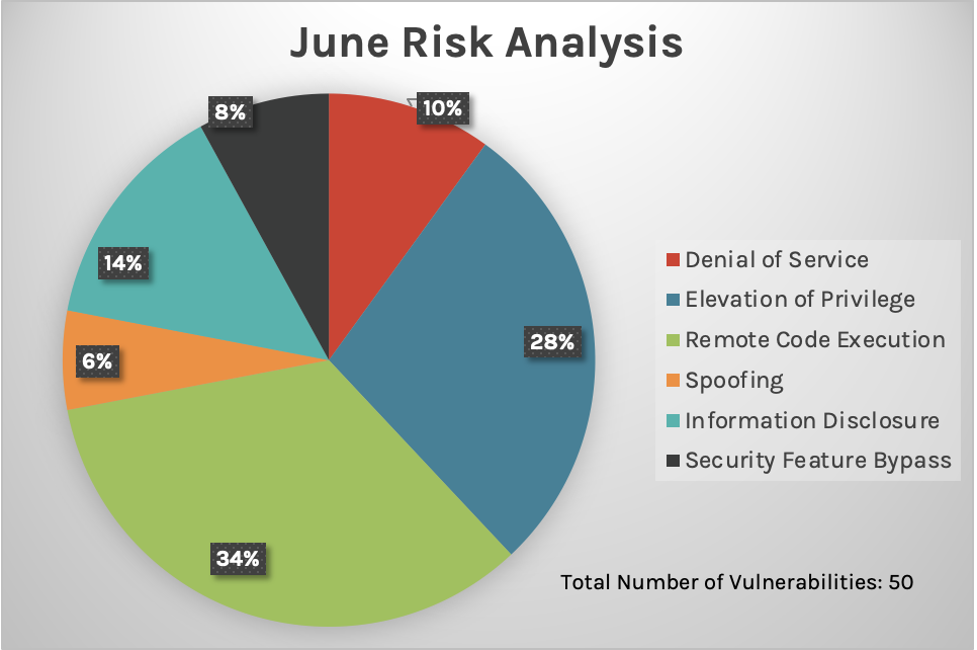
This month’s Patch Tuesday update includes fixes for 50 vulnerabilities. As with last month, it is unfortunate that Microsoft chose to patch a low quantity of vulnerabilities, considering the high number of active exploits occurring. And again we see remote code execution and elevation of privilege as the top two types of vulnerabilities, which we also saw in May. The charts below show the breakdown of impact types for May and June 2021. 
Six Vulnerabilities Exploited in the Wild
Let’s examine in detail the six in-the-wild vulnerabilities being exploited in this Patch Tuesday update.
CVE-2021-33742
CVE-2021-33742 is a Critical remote code execution vulnerability in the MSHTML engine, which powers Internet Explorer (IE). Although IE’s retirement has been announced by Microsoft, browsing activity, while low, is still active — hence we’ll likely still see patches for MSHTML. This time, we see updates for all Windows versions: 10, 8.1, 7, Server 2019, 2016, 2012 and 2008. CrowdStrike recommends patching this vulnerability first by installing applicable security updates to your platform.
CVE-2021-33739
CVE-2021-33739 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability for Microsoft DWM Core Library dwm.exe and dwmcore.dll. It was found and reported by researchers in the wild. There are indicators of it being a variant of CVE-2021-28310. The community has attributed it to the Bitter APT group (tracked by CrowdStrike as HAZY TIGER), and a security patch for CVE-2021-28310 was released in April Patch Tuesday.
CVE-2021-31955 and CVE-2021-31956
Vulnerabilities CVE-2021-31955 and CVE-2021-31956 are possibly chained together to achieve information leak and privilege escalation in the Windows Kernel context. Although the CVE-2021-31955 is only applicable to the newer Windows 10 and Server 2019, CVE-2021-31956 has patches released for as far back as Windows 7 and Server 2008.
CVE-2021-31199 and CVE-2021-31201
CVE-2021-31199 and CVE-2021-31201 are privilege escalation vulnerabilities that occur in Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider. These vulnerabilities were caught in the wild and were likely chained together with Adobe Reader CVE-2021-28550 to escape the sandbox. (Enhanced Provider is an essential part of all Windows systems that supports more robust security through longer keys.) Related patches have been rolled out for all Windows versions - 10, 8.1, 7, Server 2019, 2016, 2012, 2008. Further inspection shows that the range of attack types for this particular collection of CVEs includes a remote code execution, four privilege escalations and an information leak. Fortunately, most attackers wouldn’t be able to gain access to critical systems without an existing footprint in those systems; however, it remains vitally important to prioritize these patches to improve your security posture for hosts containing these Windows systems and applications.
| Rank | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Critical | 7.5 | CVE-2021-33742 | Windows MSHTML Platform Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Important | 8.4 | CVE-2021-33739 | Microsoft DWM Core Library Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important | 7.8 | CVE-2021-31956 | Windows NTFS Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important | 5.5 | CVE-2021-31955 | Windows Kernel Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| Important | 5.2 | CVE-2021-31199 | Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important | 5.2 | CVE-2021-31201 | Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
Four More Critical CVEs
In addition to CVE-2021-33742 already discussed, Microsoft has released patches for four more Critical CVEs. Two of these vulnerabilities, CVE-2021-31967 and CVE-2021-31985, will be updated automatically, without any action required. CVE-2021-31967 is a remote code execution vulnerability in the VP9 Video Extensions. This component is distributed from the Microsoft Store and will automatically be updated if enabled. CVE-2021-31985 is a remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft Defender. This vulnerability will only be applicable if Microsoft Defender is enabled on the system. According to Microsoft, this vulnerability will be patched under automated updates for Defender. CVE-2021-31963 is a critical remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint Server. This is one of six SharePoint vulnerabilities disclosed this month, continuing the SharePoint activity seen in recent months. The remaining SharePoint vulnerabilities have CVSS scores ranging from 5.7 to 7.6, with impacts including information disclosure, spoofing and remote code execution. It’s important to note that Microsoft released a standalone set of Sharepoint security updates to fix these vulnerabilities. These security updates are not patched by OS updates. Because of this, organizations should consider accelerating Sharepoint updates.
CVE-2021-31959 is a memory corruption vulnerability in the Scripting Engine. This vulnerability also has patches released for all Windows versions: 10, 8.1, 7, Server 2019, 2016, 2012 and 2008.
| Rank | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Critical | 7.8 | CVE-2021-31967 | VP9 Video Extensions Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 7.8 | CVE-2021-31985 | Microsoft Defender Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 7.1 | CVE-2021-31963 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 6.4 | CVE-2021-31959 | Scripting Engine Memory Corruption Vulnerability |
Other Important Vulnerabilities to Consider
| Rank | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Important | 9.4 | CVE-2021-31962 | Kerberos AppContainer Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| Important | 8.6 | CVE-2021-31977 | Windows Hyper-V Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| Important | 8.2 | CVE-2021-33741 | Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important | 8.1 | CVE-2021-31980 | Microsoft Intune Management Extension Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
The Impact and Importance of Patching
With the broad number of active, exploited vulnerabilities, organizations could be exposed unless they take an active role in patching the hosts containing the above-listed vulnerabilities. Default configuration systems are impacted and variants of the previously disclosed CVEs have been uncovered — this should alert IT staff that these vulnerabilities are not to be taken lightly. Of course, if immediate patching isn’t possible, take appropriate action to defend your hosts and servers until you can install the proper security updates. Finally, if you have hosts still using Internet Explorer, take action to sunset the browser completely.
Learn More
Watch this video on Falcon Spotlight™ vulnerability management to see how you can quickly monitor and prioritize vulnerabilities within the systems and applications in your organization.
About CVSS Scores
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a free and open industry standard that CrowdStrike and many other cybersecurity organizations use to assess and communicate software vulnerabilities’ severity and characteristics. The CVSS Base Score ranges from 0.0 to 10.0, and the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) adds a severity rating for CVSS scores. Learn more about vulnerability scoring in this article.
Additional Resources
- Learn more on how Falcon Spotlight can help you discover and manage vulnerabilities in your environments.
- See how Falcon Complete stops Microsoft exchange server zero-day exploits.
- Make prioritization painless and efficient. Watch how Falcon Spotlight enables IT staff to improve visibility with custom filters and team dashboards.
- Read last month’s Patch Tuesday for more information on critical vulnerabilities your organization should prioritize.
- Learn about the recent Baron Samedit vulnerability and CrowdStrike’s custom dashboard.
- Test CrowdStrike next-gen AV for yourself. Start your free trial of Falcon Prevent™ today.






![Helping Non-Security Stakeholders Understand ATT&CK in 10 Minutes or Less [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/video-ATTCK2-1?wid=530&hei=349&fmt=png-alpha&qlt=95,0&resMode=sharp2&op_usm=3.0,0.3,2,0)
![Qatar’s Commercial Bank Chooses CrowdStrike Falcon®: A Partnership Based on Trust [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/Edward-Gonam-Qatar-Blog2-1?wid=530&hei=349&fmt=png-alpha&qlt=95,0&resMode=sharp2&op_usm=3.0,0.3,2,0)





















































